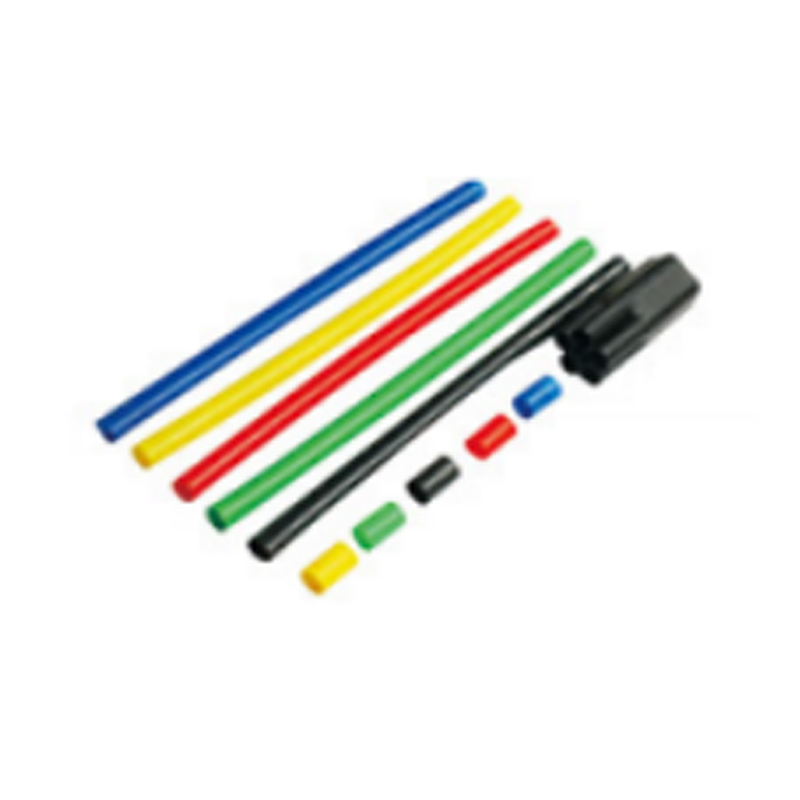
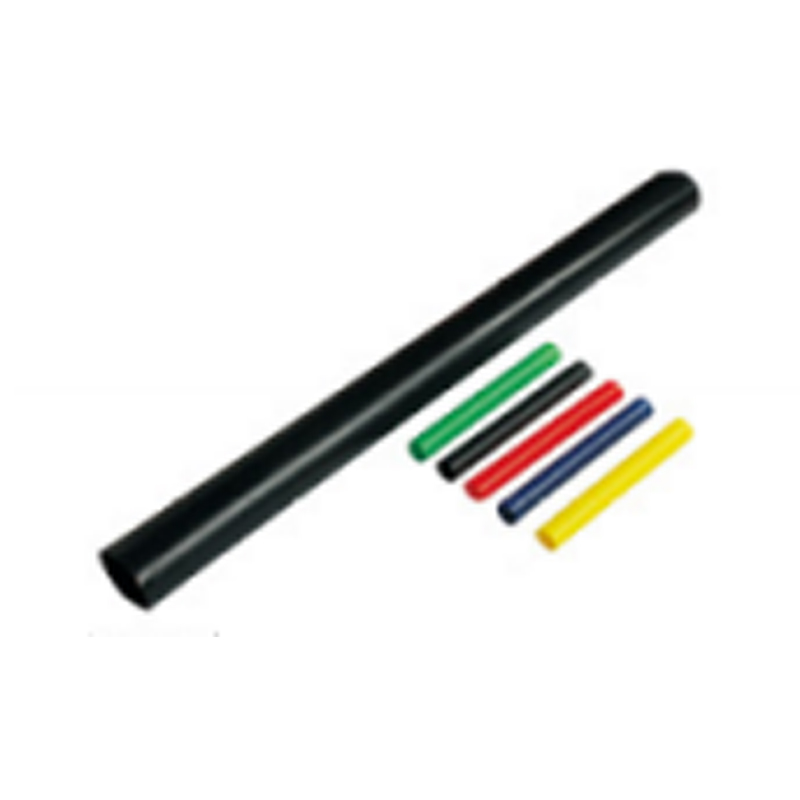
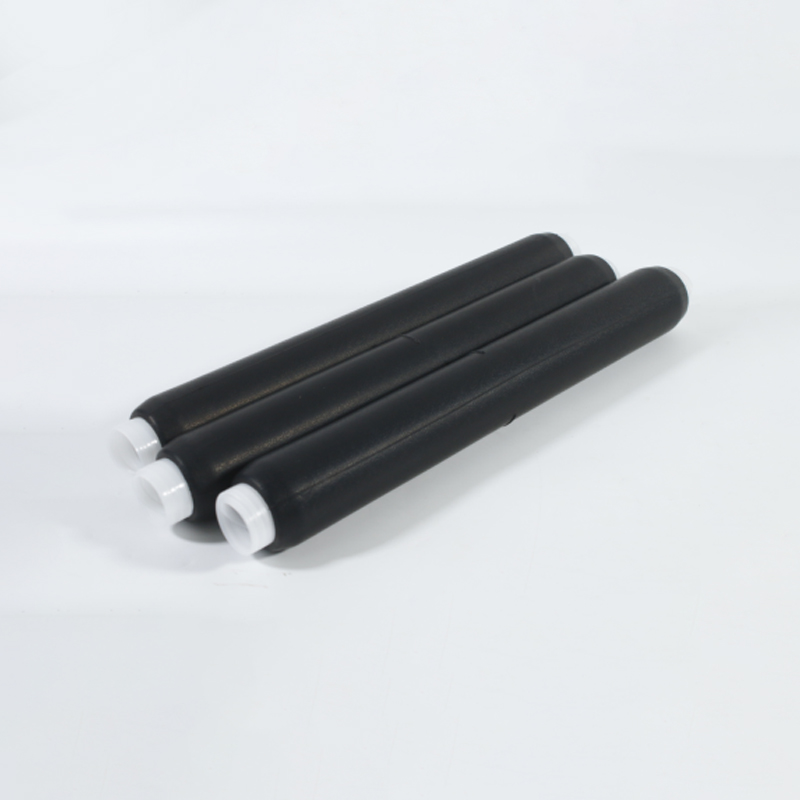
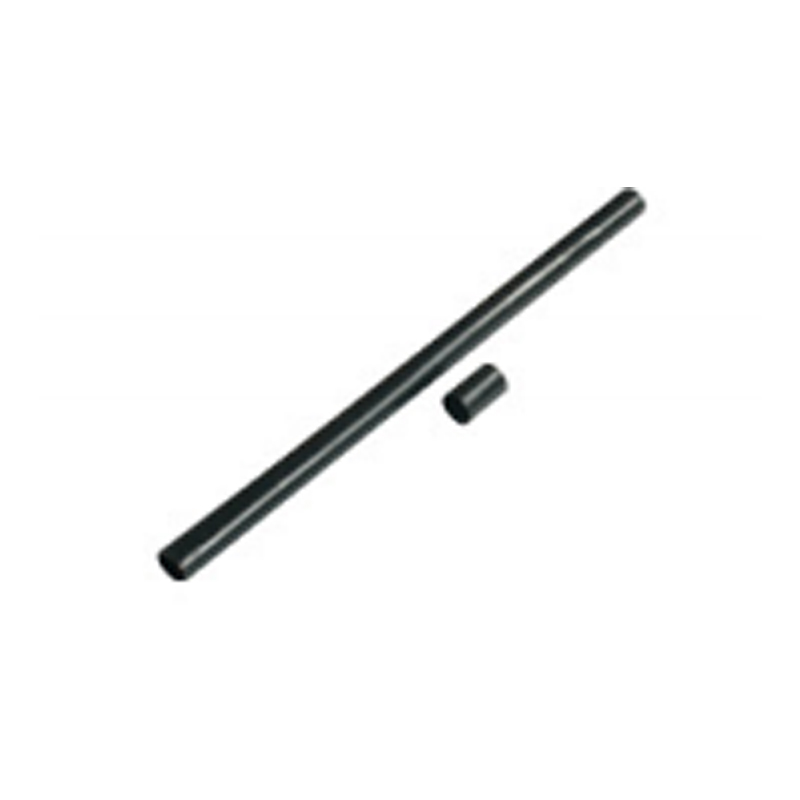
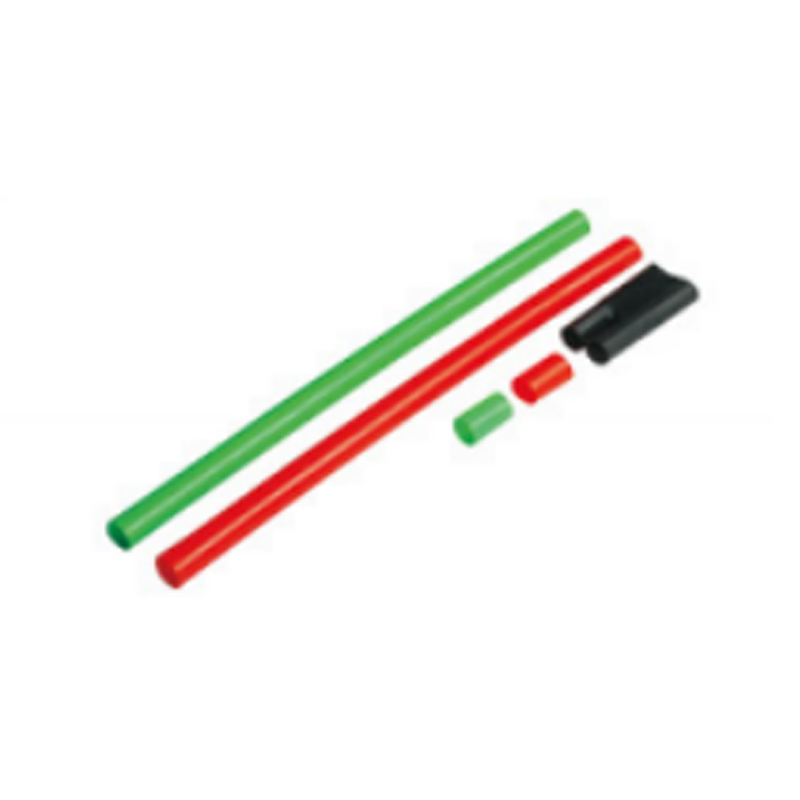
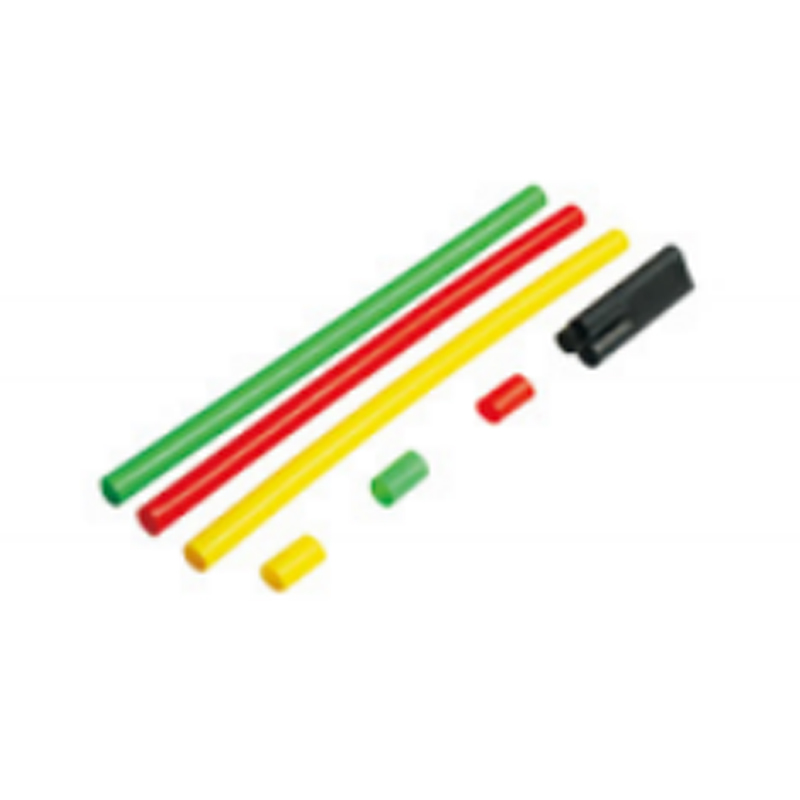
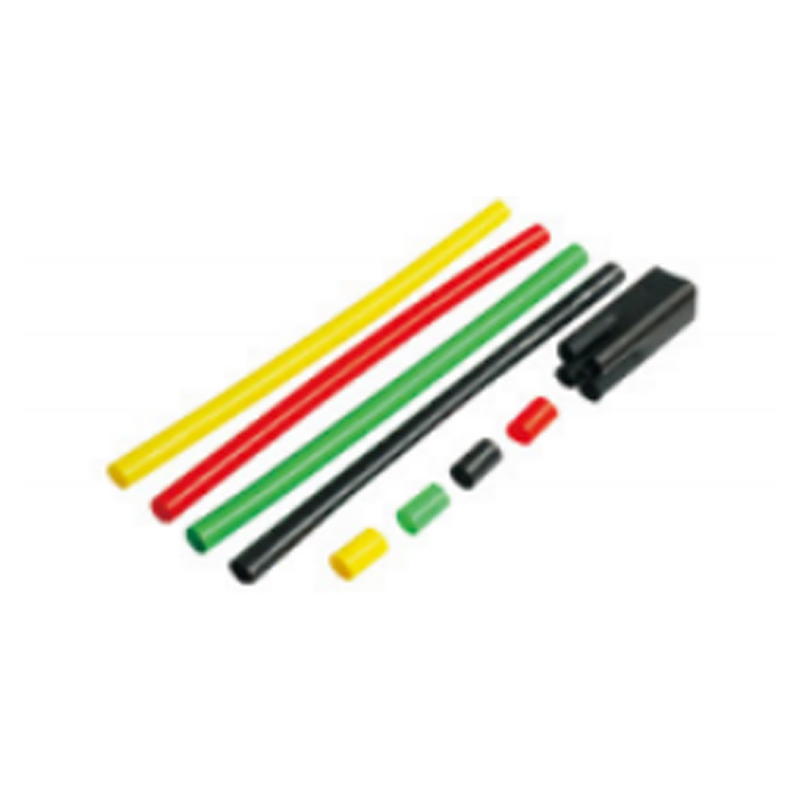
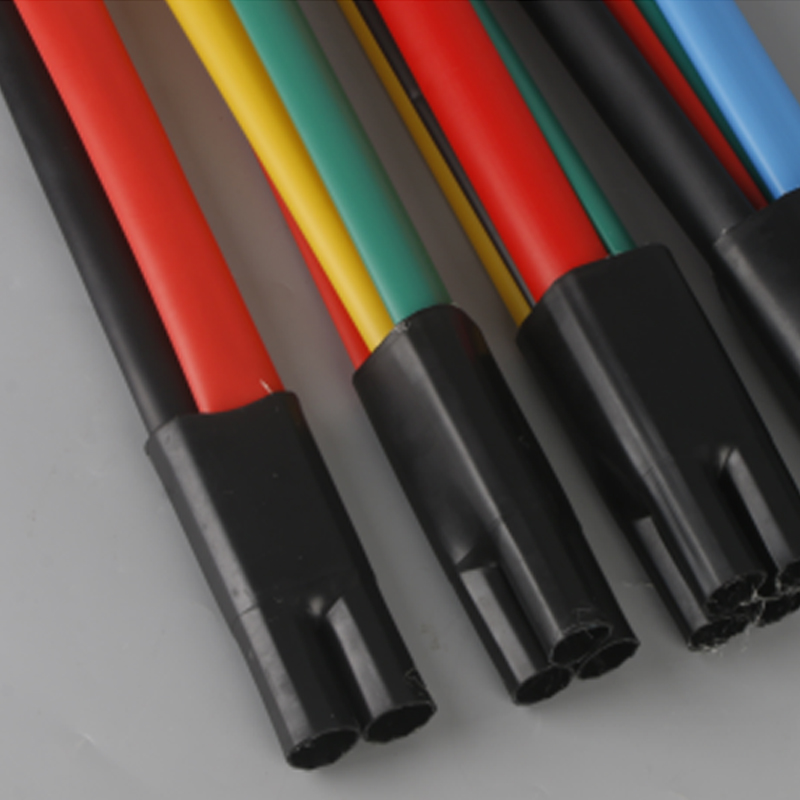
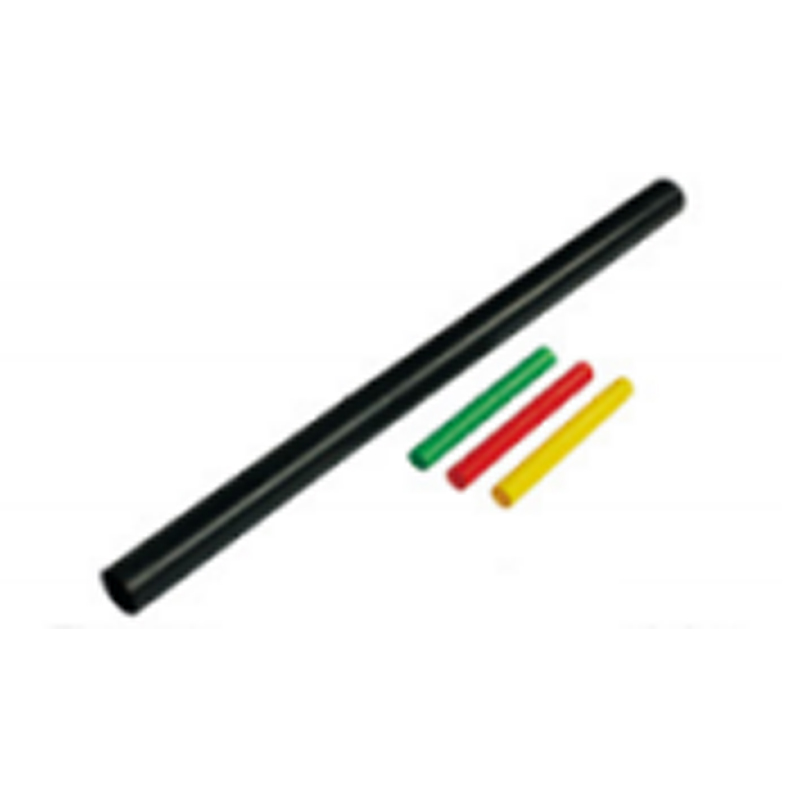
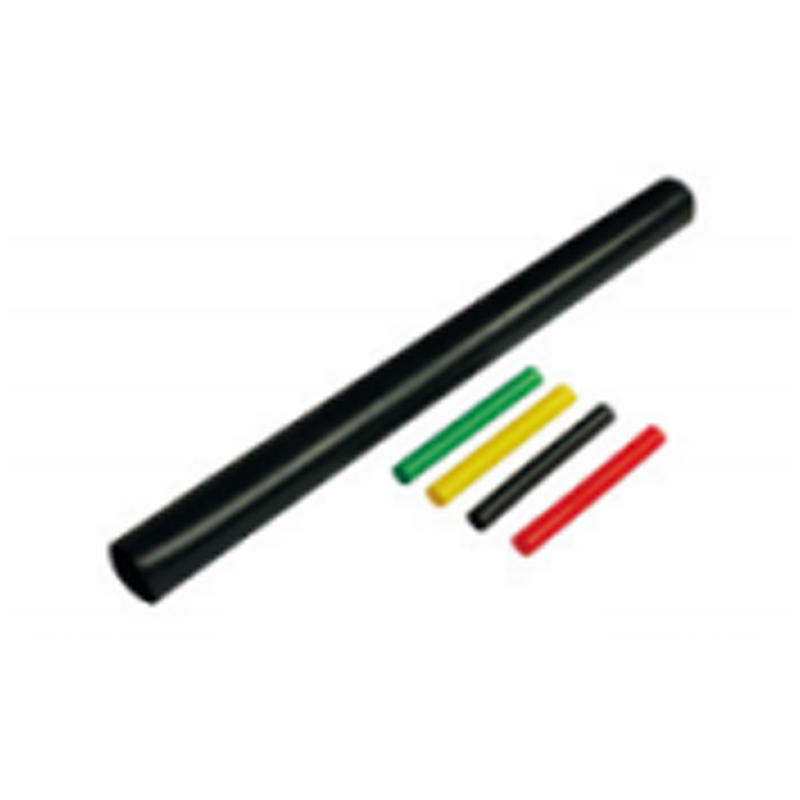
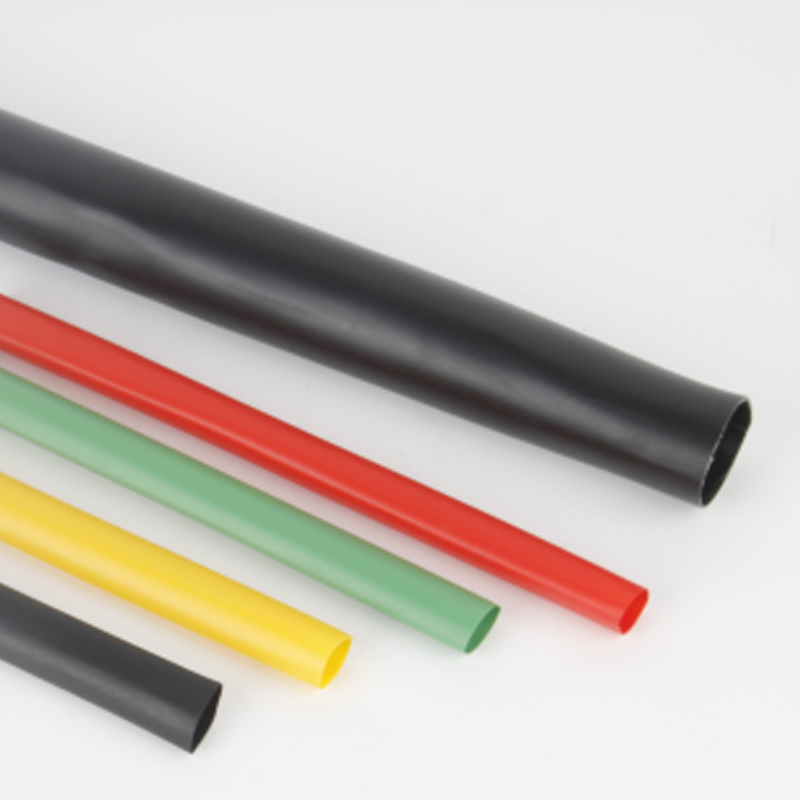
| Photograph | Model | The application of the cable section | Unit | Insulation tube length(mm) |
| Single-core cable termination | SY-1/1.0 | 10月16日 | overlap set | 600 800 1000 |
| SY-1/1.1 | 25-50 | overlap set | ||
| SY-1/1.2 | 70-120 | overlap set | ||
| SY-1/1.3 | 150-240 | overlap set | ||
| SY-1/1.4 | 300-500 | overlap set | ||
| Two-core cable termination | SY-1/2.0 | 10月16日 | overlap set | |
| SY-1/2.1 | 25-50 | overlap set | ||
| SY-1/2.2 | 70-120 | overlap set | ||
| SY-1/2.3 | 150-240 | overlap set | ||
| SY-1/2.4 | 300-500 | overlap set | ||
| Three-core cable termination | SY-1/3.0 | 10月16日 | overlap set | |
| SY-1/3.1 | 25-50 | overlap set | ||
| SY-1/3.2 | 70-120 | overlap set | ||
| SY-1/3.3 | 150-240 | overlap set | ||
| SY-1/3.4 | 300-500 | overlap set | ||
| Four-core cable termination | SY-1/4.0 | 10月16日 | overlap set | |
| SY-1/4.1 | 25-50 | overlap set | ||
| SY-1/4.2 | 70-120 | overlap set | ||
| SY-1/4.3 | 150-240 | overlap set | ||
| SY-1/4.4 | 300-500 | overlap set | ||
| Five-core cable terminal | SY-1/5.0 | 10月16日 | overlap set | |
| SY-1/5.1 | 25-50 | overlap set | ||
| SY-1/5.2 | 70-120 | overlap set | ||
| SY-1/5.3 | 150-240 | overlap set | ||
| SY-1/5.4 | 300-500 | overlap set |
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Heat Shrink Termination Manufacturer
1KV Heat Shrinkable Cable Termination
1KV Heat Shrink Intermediate Cable Connector
| Photograph | Model | The application of the cable section | Unit | Insulation tube length(mm) |
| Single-core cable intermediate joint | SY-1/1.0 | 10-16 | Overlap set | 1000 |
| SY-1/1.1 | 25-50 | Overlap set | ||
| SY-1/1.2 | 70-120 | Overlap set | ||
| SY-1/1.3 | 150-240 | Overlap set | ||
| SY-1/1.4 | 300-500 | Overlap set | ||
| Intermediate joint of two core cable | SY-1/2.0 | 10-16 | Overlap set | |
| SY-1/2.1 | 25-50 | Overlap set | ||
| SY-1/2.2 | 70-120 | Overlap set | ||
| SY-1/2.3 | 150-240 | Overlap set | ||
| SY-1/2.4 | 300-500 | Overlap set | ||
| Three-core cable intermediate joint | SY-1/3.0 | 10-16 | Overlap set | |
| SY-1/3.1 | 25-50 | Overlap set | ||
| SY-1/3.2 | 70-120 | Overlap set | ||
| SY-1/3.3 | 150-240 | Overlap set | ||
| SY-1/3.4 | 300-500 | Overlap set | ||
| Intermediate joint of four core cable | SY-1/4.0 | 10-16 | Overlap set | |
| SY-1/4.1 | 25-50 | Overlap set | ||
| SY-1/4.2 | 70-120 | Overlap set | ||
| SY-1/4.3 | 150-240 | Overlap set | ||
| SY-1/4.4 | 300-500 | Overlap set | ||
| The intermediate joint of the five-core cable | SY-1/5.0 | 10-16 | Overlap set | |
| SY-1/5.1 | 25-50 | Overlap set | ||
| SY-1/5.2 | 70-120 | Overlap set | ||
| SY-1/5.3 | 150-240 | Overlap set | ||
| SY-1/5.4 | 300-500 | Overlap set |
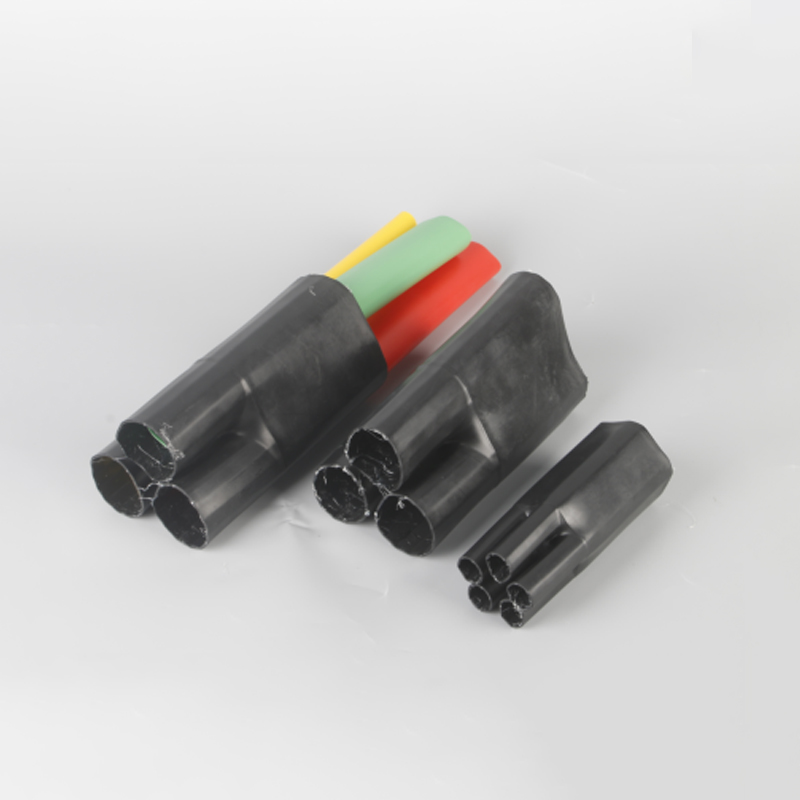
1KV Heat Srhinkable Wire Branch
| Name | Model | Applicable cable section(mm) | Unit |
| Two core | ZT-2.0 | 10-16 | only |
| ZT-2.1 | 25-50 | only | |
| ZT-2.2 | 70-120 | only | |
| ZT-2.3 | 150-240 | only | |
| Three core | ZT-3.0 | 10-16 | only |
| ZT-3.1 | 25-50 | only | |
| ZT-3.2 | 70-120 | only | |
| ZT-3.3 | 150-240 | only | |
| ZT-3.4 | 300-400 | only | |
| Four core | ZT-4.0 | 10-16 | only |
| ZT-4.1 | 25-50 | only | |
| ZT-4.2 | 70-120 | only | |
| ZT-4.3 | 150-240 | only | |
| ZT-4.4 | 300-400 | only | |
| Five core | ZT-5.0 | 10-16 | only |
| ZT-5.1 | 25-50 | only | |
| ZT-5.2 | 70-120 | only | |
| ZT-5.3 | 150-240 | only | |
| ZT-5.4 | 300-400 | only |
Heat-shrinkable cable termination is a type of electrical connector designed to insulate and protect the exposed ends of cables, particularly power cables. It consists of a heat-shrinkable sleeve made from polymer materials, such as cross-linked polyolefin, that shrinks when exposed to heat, forming a tight, waterproof, and insulated seal around the cable. The primary function of this termination is to provide mechanical strength, electrical insulation, and environmental protection for the cable’s exposed end.
1. Key Components and Features
Heat Shrink Tubing: The primary component of the termination is the heat shrink tubing, which is designed to shrink in size when exposed to heat. The tubing typically comes with a dual-layer structure, with an outer layer for mechanical protection and an inner adhesive layer that bonds with the cable to prevent water ingress.
Insulating Layers: Inside the heat shrink tubing, there are usually insulating layers, including a conductive material for stress control, which helps to spread electrical stresses evenly across the cable termination area.
Cable Preparation: The cable is first stripped of its outer sheath and insulation at the termination point. A stress relief element may be applied to ensure that no electrical field concentration occurs at the point where the termination connects to the cable.
Shrinkage and Sealing: Upon heating, the heat shrink tubing reduces in diameter, tightly encapsulating the cable end. The adhesive layer melts and bonds with the cable, ensuring that the termination is waterproof and prevents any moisture from entering the cable core.
2. Installation Process
The installation of heat-shrinkable cable terminations is a straightforward process that can be broken down into several steps:
Preparation of the Cable: The first step involves stripping the outer sheath of the cable to expose the conductors, followed by the removal of any additional insulation layers.
Placement of the Heat Shrink Sleeve: Once the cable is prepared, the heat shrinkable sleeve is slid over the exposed conductors. The sleeve should be sized correctly to ensure a tight fit once it shrinks.
Application of Heat: Using a heat gun or specialized heat source, heat is applied to the heat-shrinkable sleeve. The tubing shrinks evenly over the cable, ensuring a tight fit and forming a waterproof seal around the cable’s exposed end.
Final Inspection: After the termination has cooled and hardened, a final inspection should be conducted to ensure the termination is secure and there are no gaps or exposed areas.
3. Applications
Heat-shrinkable cable terminations are used in various applications, including:
Power Distribution Networks: These terminations are frequently used in high-voltage power distribution networks to protect the cable ends in substations, transformers, and switchgear equipment.
Telecommunications: In telecom installations, heat-shrinkable terminations are used to ensure the protection and longevity of cables that are exposed to varying environmental conditions.
Industrial and Offshore Applications: These terminations are particularly useful in industries such as oil and gas, where cables are exposed to extreme weather, high humidity, and chemical exposure.
Transportation: Heat-shrinkable terminations are used in automotive, railway, and aviation industries to protect critical wiring systems from environmental damage, moisture, and mechanical stresses.
Whether used in power distribution, telecommunications, or industrial settings, heat-shrinkable terminations are an indispensable component in ensuring the longevity and safety of electrical systems.

About Us
Honor
-
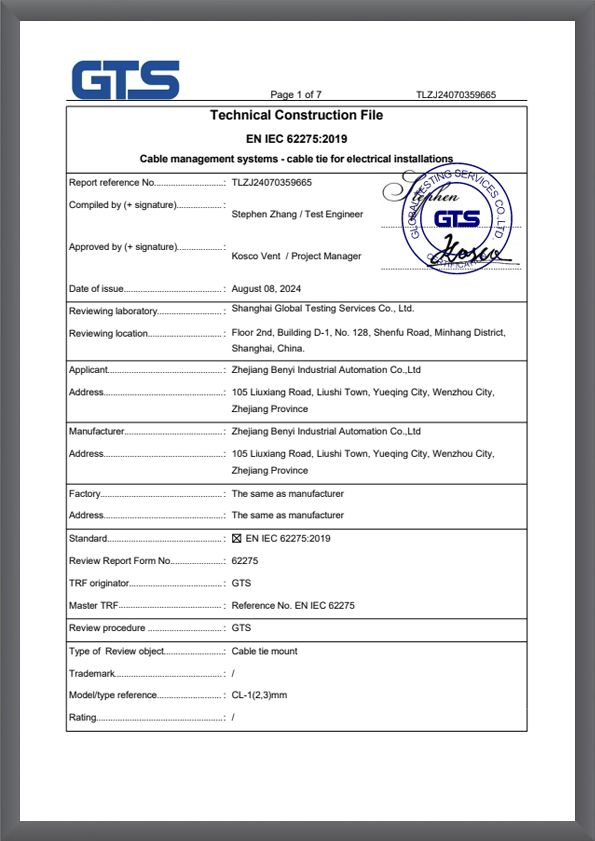 TLZJ24070359665
TLZJ24070359665 -
 CLZJ24070359665
CLZJ24070359665 -
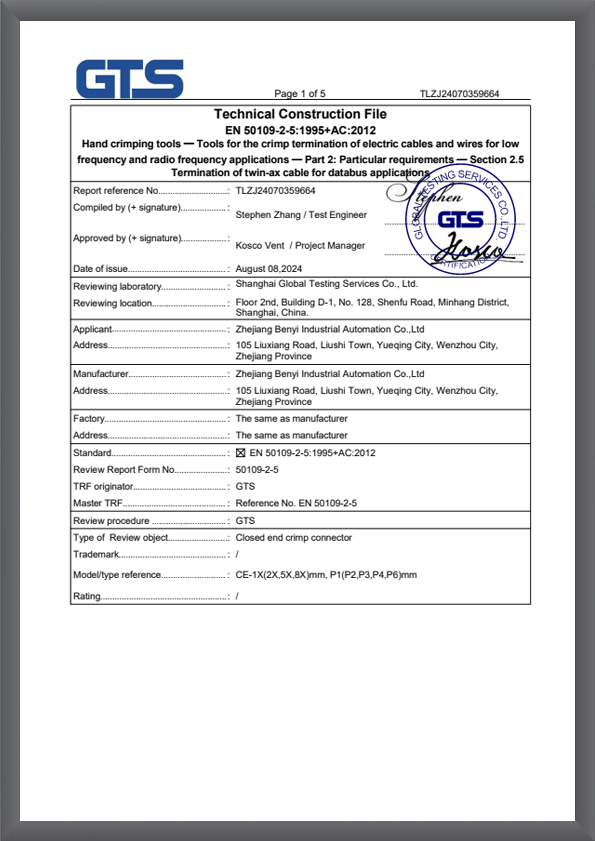 TLZJ24070359664
TLZJ24070359664 -
 CLZJ24070359664
CLZJ24070359664 -
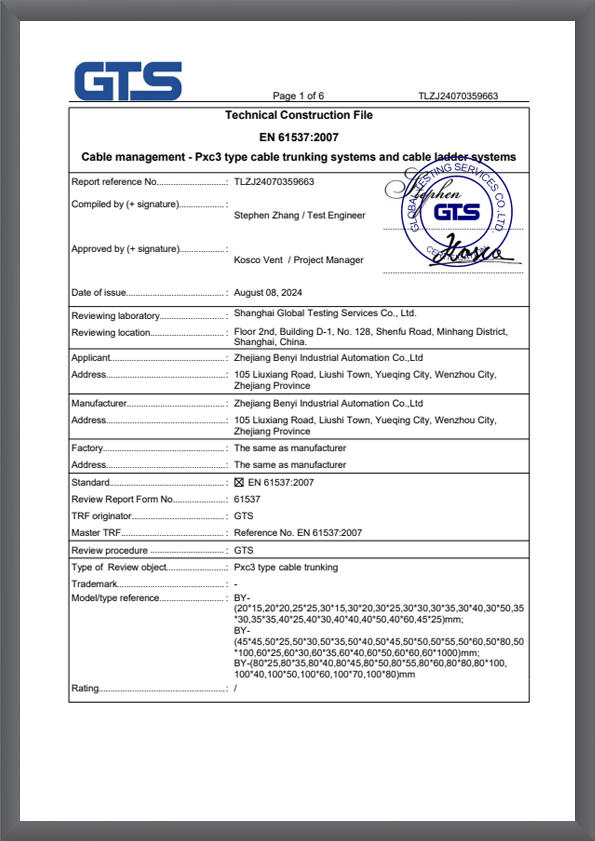 TLZJ24070359663
TLZJ24070359663 -
 CLZJ24070359663
CLZJ24070359663
News
-
Industry News 2026-02-13
Copper terminals and lugs are common components in electrical distribution and wiring systems, serving both conductivity and mechanical connection pur...
View More -
Industry News 2026-02-06
Cold-pressed insulated terminals are widely used in electrical systems to provide secure and reliable wire connections. These terminals are manufactur...
View More -
Industry News 2026-01-30
2:1 heat shrink tubes are widely used in industrial and electronic applications due to their ability to provide electrical insulation, mechanical prot...
View More -
Industry News 2026-01-23
Brass cable glands are essential components in industrial electrical systems. They secure cables as they enter equipment or enclosures, providing stra...
View More
Contact us now

 +86-15558905711
+86-15558905711 +86-15057372736
+86-15057372736 [email protected]
[email protected] 105 Liuxiang Road, Liushi Town, Yueqing City, Wenzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
105 Liuxiang Road, Liushi Town, Yueqing City, Wenzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
 英语
英语 中文简体
中文简体 俄语
俄语 西班牙语
西班牙语














