Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Cold-Pressed Insulated Terminals Improve Electrical Connections
Cold-pressed insulated terminals are widely used in electrical systems to provide secure and reliable wire connections. These terminals are manufactured by compressing copper or aluminum components around conductors without the need for soldering, which ensures a tight and stable electrical contact. The insulation covering protects against accidental short circuits and helps maintain long-term safety.
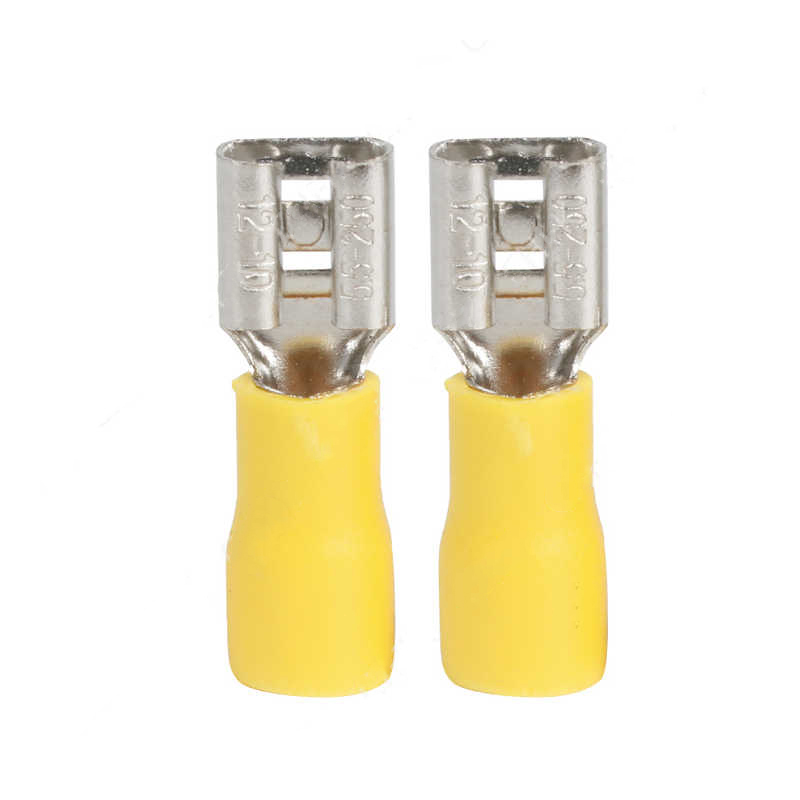

In practice, these terminals are available in a variety of shapes, including ring, spade, fork, and pin types. Each type is designed to accommodate different wire gauges and installation requirements. The cold-pressing process forms a permanent bond between the terminal and the conductor, which reduces the risk of loosening or failure due to vibration or thermal cycling. Manufacturers often provide terminals with color-coded insulation to indicate wire sizes, which simplifies installation and reduces potential errors during assembly.
Safety and performance are key considerations when selecting cold-pressed insulated terminals. The insulation material provides resistance to heat and electrical stress, ensuring stable operation over extended periods. In industrial settings, these terminals are often used in control panels, automotive wiring, and heavy machinery connections, where reliable conductivity and mechanical stability are essential. Quality checks typically include inspection for dimensional accuracy, compression integrity, and electrical resistance to meet operational standards.
Maintenance of cold-pressed insulated terminals is generally minimal, but periodic inspection is important to ensure consistent performance. Terminals may be exposed to moisture, dust, or temperature changes that can cause minor corrosion or loosening over time. Regular checks confirm that each terminal remains properly seated, the insulation is intact, and the wire-to-terminal connection is secure. These inspections are especially useful in industrial or outdoor environments, where conditions may accelerate wear.
Using the correct crimping tools and techniques is important for achieving proper compression and reliable electrical conductivity. The crimping process forms a stable bond between the terminal and the wire, which affects both electrical flow and mechanical stability. If the tools are not matched to the terminal size or the wire, incomplete compression can occur, increasing resistance or causing localized heating during operation. Such conditions may reduce system efficiency or create safety concerns.
Selecting the appropriate terminal size and type for the wire and application is also essential. Ring, spade, fork, or pin terminals serve different functions, and choosing a match helps prevent over-compression or stress on the wire. Many terminals have color-coded insulation to indicate compatible wire gauges, making installation more straightforward and reducing errors across multiple connections.
Cold-pressed insulated terminals are used widely in residential, commercial, and industrial electrical systems. Their combination of mechanical bonding, electrical conductivity, and insulation protection makes them suitable for applications such as household wiring, automotive electrical systems, control panels, and machinery connections. They are designed to withstand vibration, thermal cycling, and typical electrical load, helping maintain consistent performance over time.
Overall, cold-pressed insulated terminals are an important component in modern electrical systems. With proper installation, routine inspection, and attention to environmental factors, these terminals provide reliable connections, support stable electrical flow, and help maintain safety in a variety of wiring applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the main function of cold-pressed insulated terminals?
A: They provide secure, insulated connections between wires and electrical components.
Q: What types of terminals are commonly used?
A: Ring, spade, fork, and pin types.
Q: How is installation achieved?
A: Through cold-pressing or crimping the terminal onto the conductor.
Q: Do these terminals require maintenance?
A: Minimal maintenance is needed, mostly periodic inspection for corrosion or loosening.
Q: Where are these terminals typically applied?
A: In household wiring, automotive systems, industrial control panels, and machinery connections.
News categories
Exhibition Information
Related Products

 +86-15558905711
+86-15558905711 +86-15057372736
+86-15057372736 [email protected]
[email protected] 105 Liuxiang Road, Liushi Town, Yueqing City, Wenzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
105 Liuxiang Road, Liushi Town, Yueqing City, Wenzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
 英语
英语 中文简体
中文简体 俄语
俄语 西班牙语
西班牙语











