Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Copper Terminal Copper Lugs Ensure Reliable Conductivity
Copper terminals and lugs are common components in electrical distribution and wiring systems, serving both conductivity and mechanical connection purposes. Made from high-purity copper, these components conduct electricity efficiently while limiting energy loss across circuits. Many are coated with tin to reduce corrosion, especially in areas exposed to moisture or temperature changes. The design helps conductors connect to busbars, switches, and other electrical equipment safely, supporting consistent operation in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
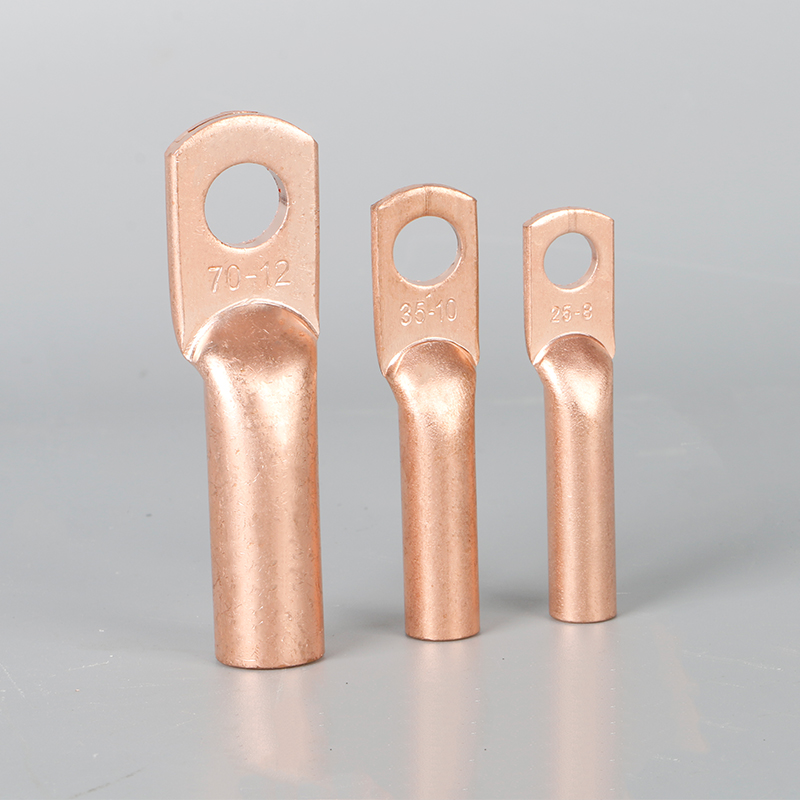

These components come in different shapes and sizes to match various wiring needs. Ring, fork, and tubular lugs fit different wire gauges and installation methods, while some designs accommodate connections between copper and aluminum conductors. Installation generally involves crimping or bolting the lug to the wire, which maintains electrical contact and physical support. Routine inspection for corrosion, wear, or loosening can help ensure proper performance across applications, from household wiring to industrial machinery.
These lugs are available in various shapes and sizes, including ring, fork, and tubular types, to accommodate different wire gauges and connection requirements. Proper selection of lug size is critical to ensure a tight fit and stable electrical contact. In addition, some copper terminals are designed for use with aluminum-copper transitions, which prevent galvanic corrosion when connecting dissimilar metals.
In addition to electrical conductivity, copper lugs are valued for their durability under mechanical stress. They can withstand repeated thermal cycling and vibration, which makes them suitable for use in power distribution panels, automotive wiring harnesses, and renewable energy installations. Installation involves precise crimping or bolting, ensuring a firm connection and preventing potential failures due to loose contacts. Routine inspections typically include checking for signs of corrosion, deformation, or inadequate compression.
Copper terminals contribute to safety in electrical systems by helping maintain consistent electrical connections and low resistance paths. When properly installed, these lugs reduce the potential for localized heating, which can occur if connections are loose or corroded, lowering the risk of overheating or fire hazards. The design and material properties of copper terminals allow them to handle substantial current loads. This makes them suitable for use in high-current circuits and critical power distribution applications.
These terminals are widely applied in industrial machinery, power distribution panels, automotive wiring, and renewable energy systems. Their mechanical strength ensures that conductors remain securely attached under vibration or thermal cycling, while tin plating or other coatings protect against corrosion. Electrical engineers and contractors often select copper terminals to meet system specifications that require stable connections and predictable performance, supporting installation practices that emphasize safety and functional consistency. Routine inspection and proper installation techniques further enhance their effectiveness in maintaining secure and functional wiring systems.
Copper terminal copper lugs remain a vital component in both industrial and residential wiring systems. Their combination of high conductivity, mechanical stability, and compatibility with various conductors ensures safe and reliable connections across a wide range of applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the primary function of copper lugs?
A: To provide secure electrical connections with high conductivity.
Q: What shapes are commonly available?
A: Ring, fork, and tubular types.
Q: Can copper lugs connect different metals?
A: Yes, some are designed for aluminum-copper transitions.
Q: How is installation performed?
A: Through crimping, bolting, or cold-pressing.
Q: Where are copper lugs commonly used?
A: Power distribution, automotive wiring, and renewable energy installations.
News categories
Exhibition Information
Related Products

 +86-15558905711
+86-15558905711 +86-15057372736
+86-15057372736 [email protected]
[email protected] 105 Liuxiang Road, Liushi Town, Yueqing City, Wenzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
105 Liuxiang Road, Liushi Town, Yueqing City, Wenzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
 英语
英语 中文简体
中文简体 俄语
俄语 西班牙语
西班牙语











