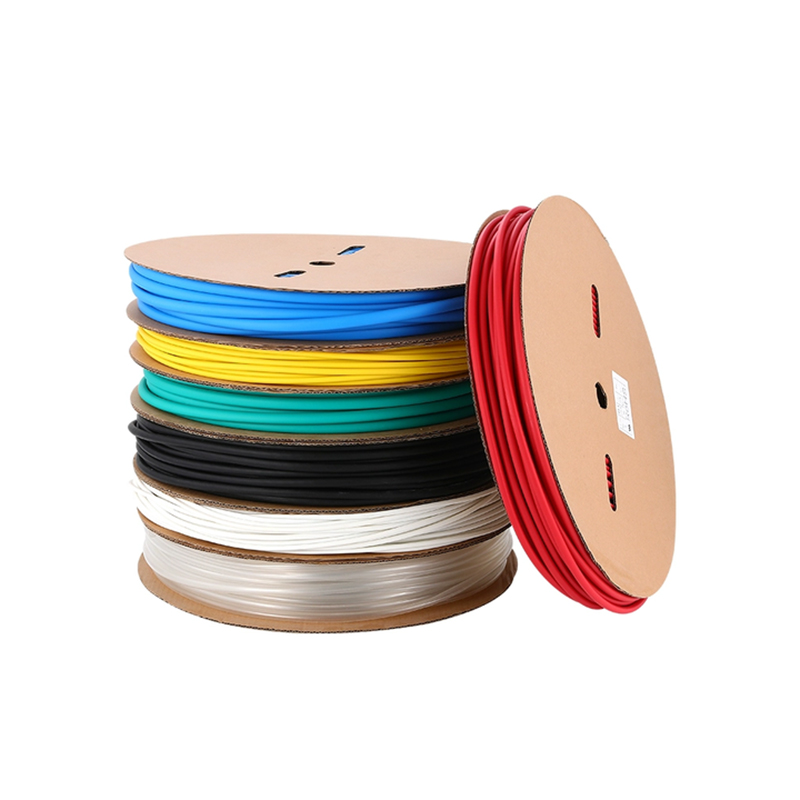
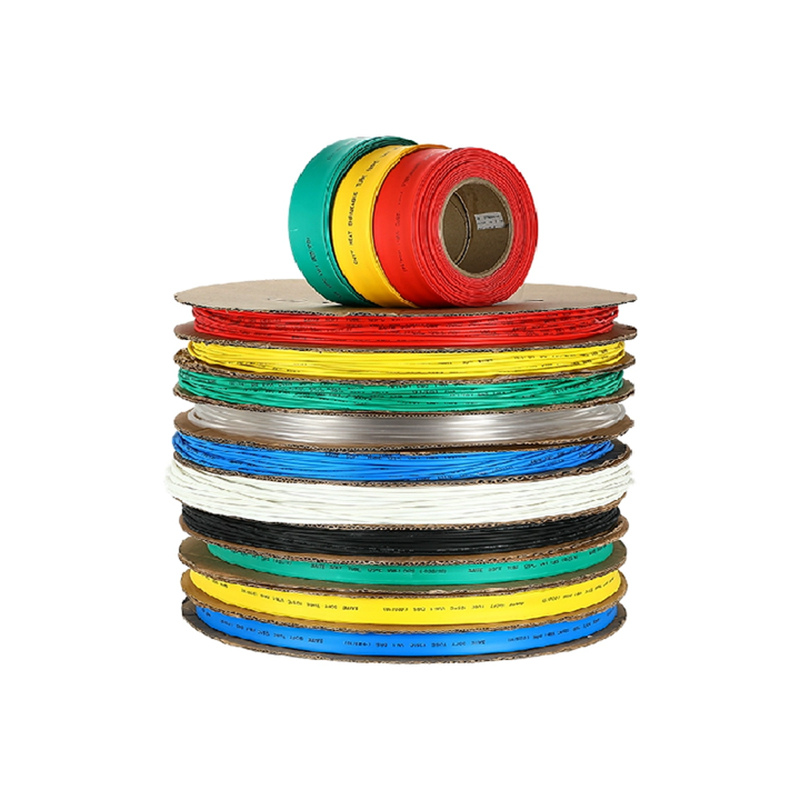
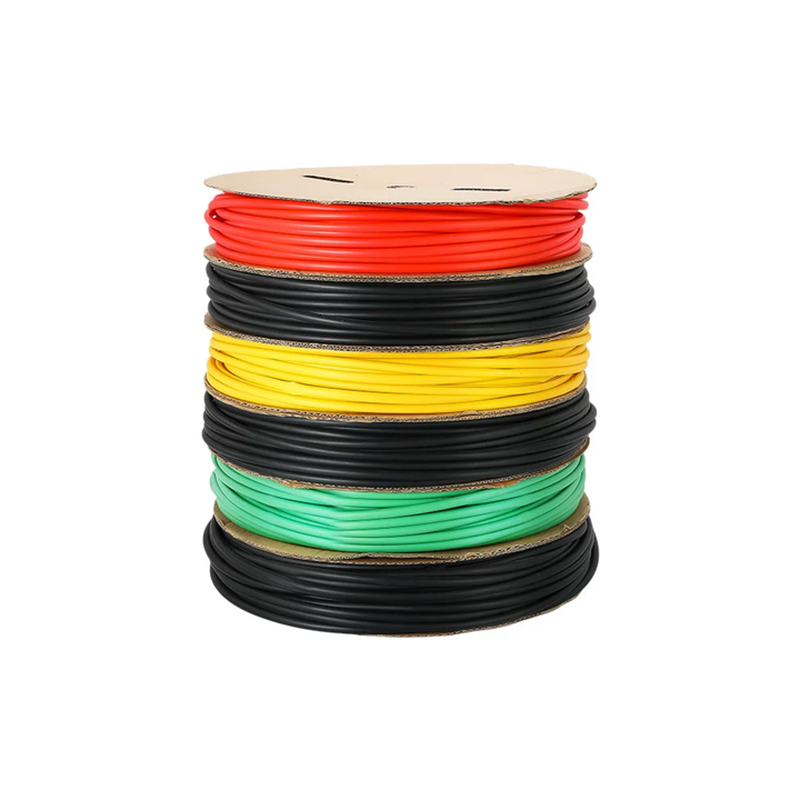
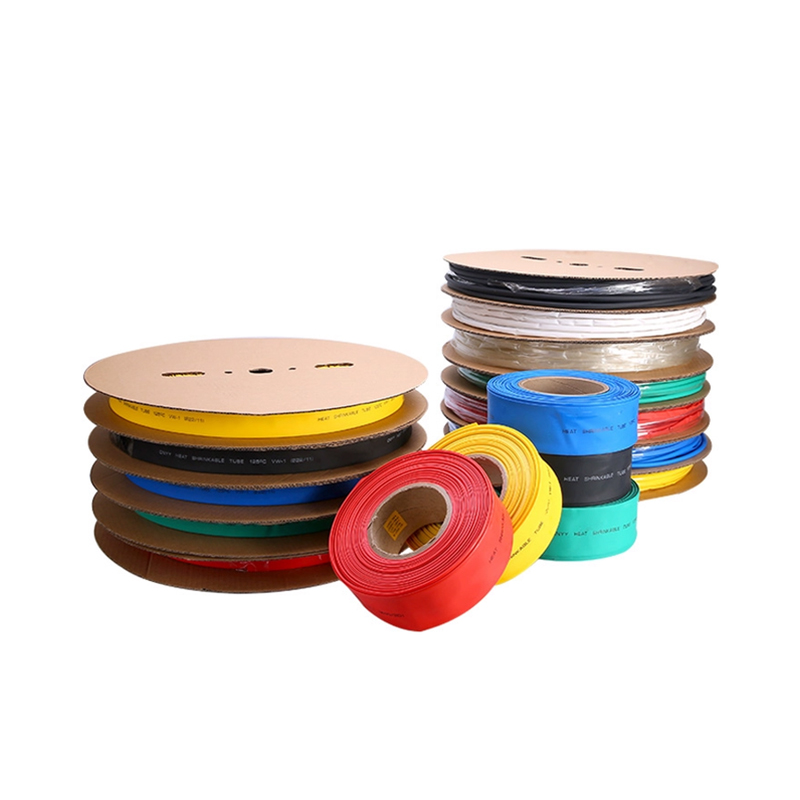
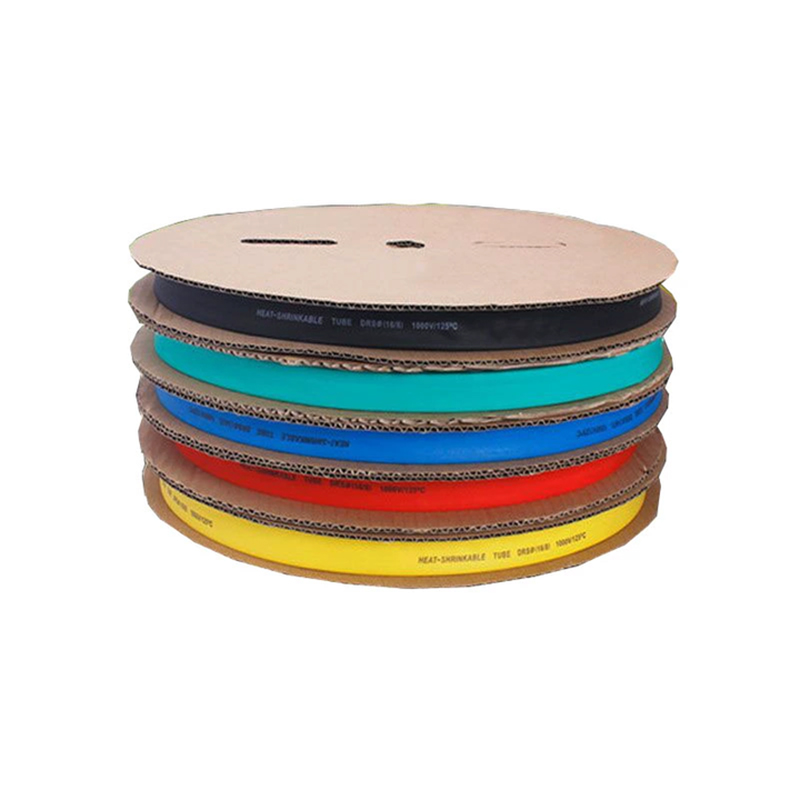
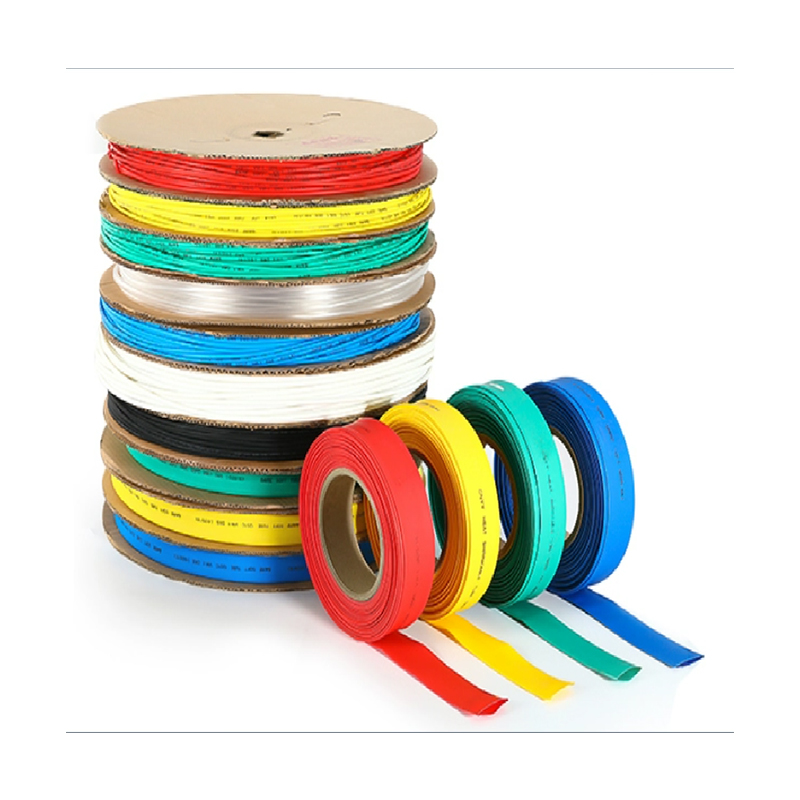
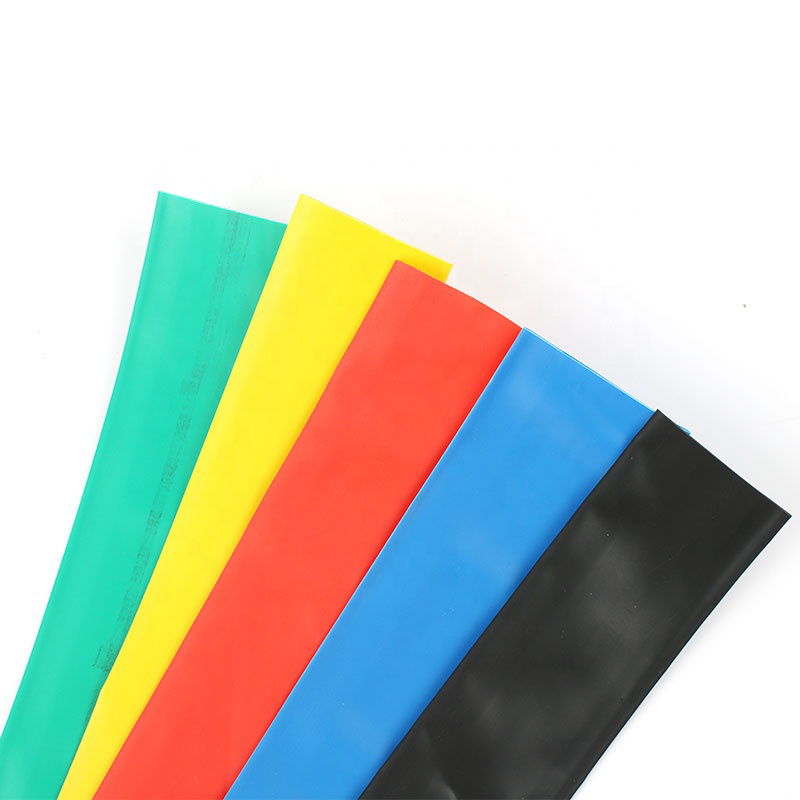
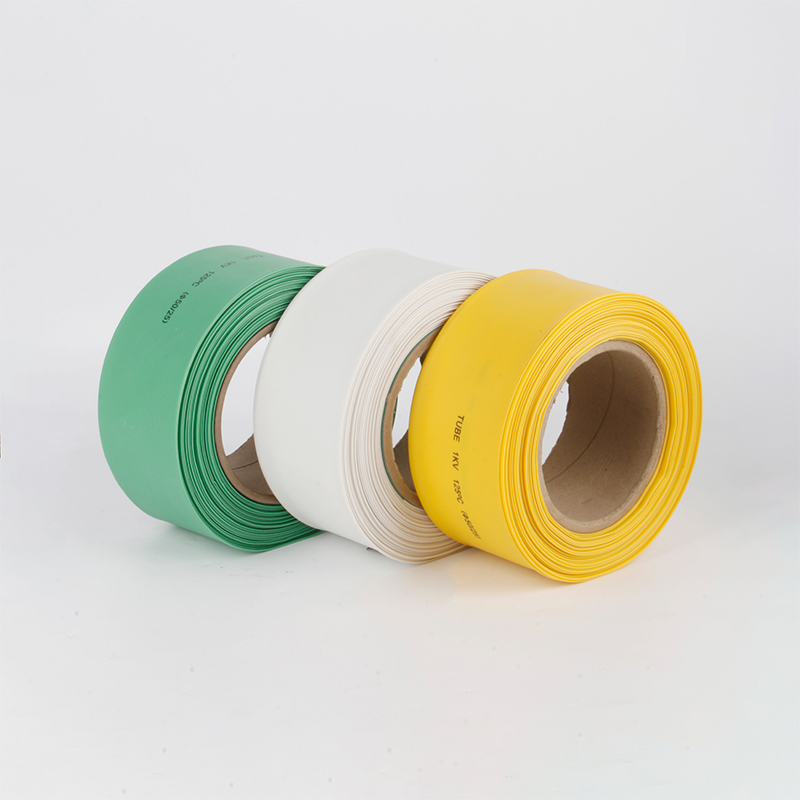
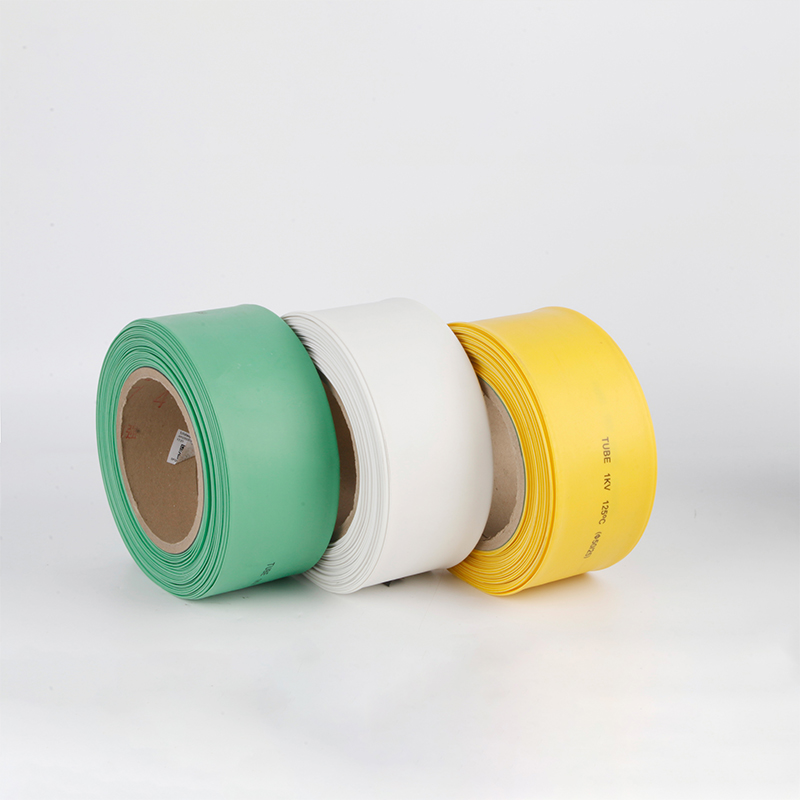
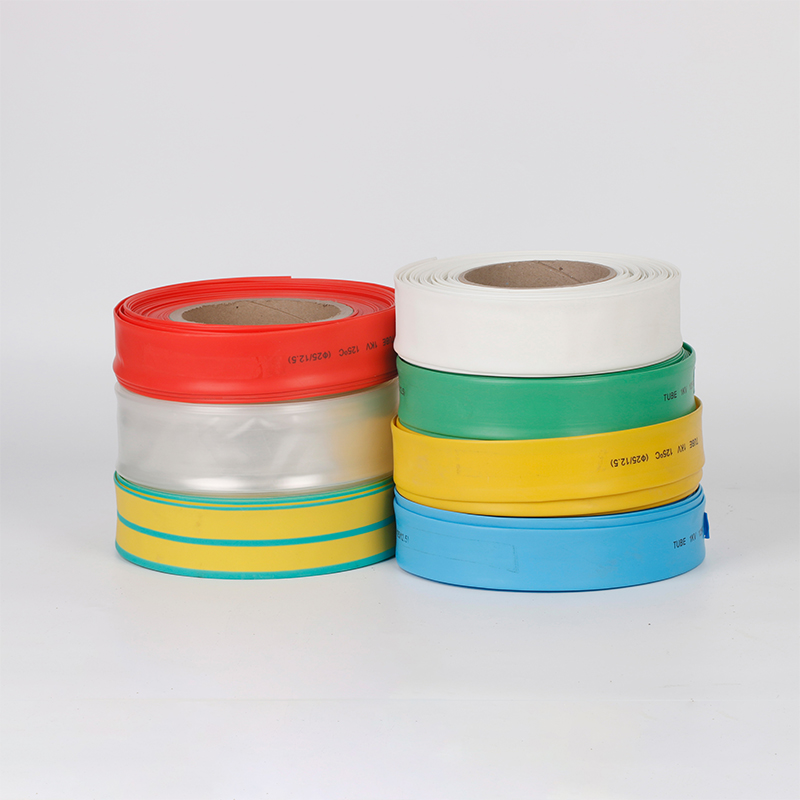
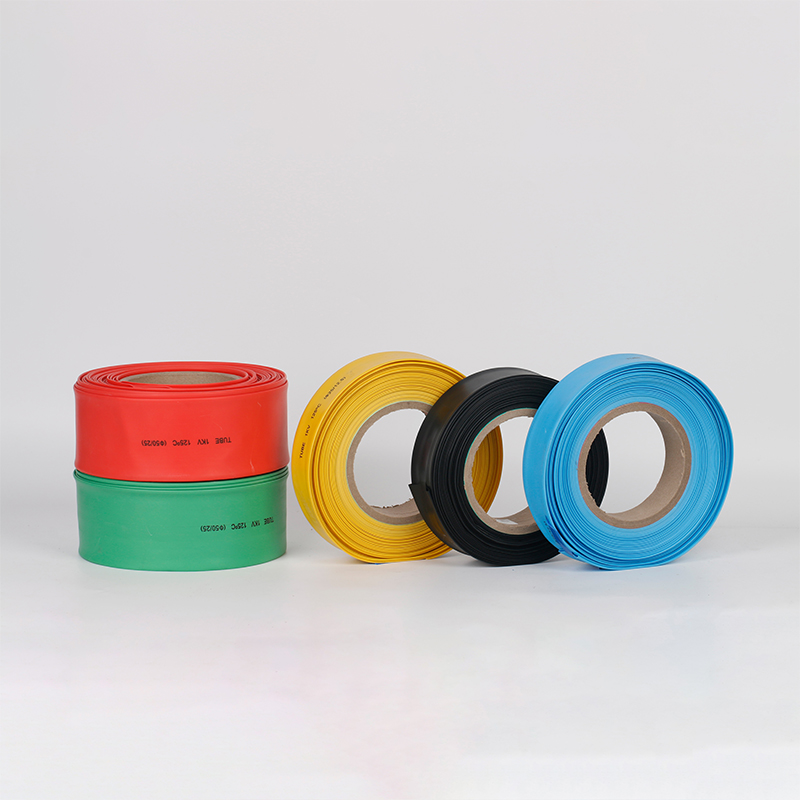
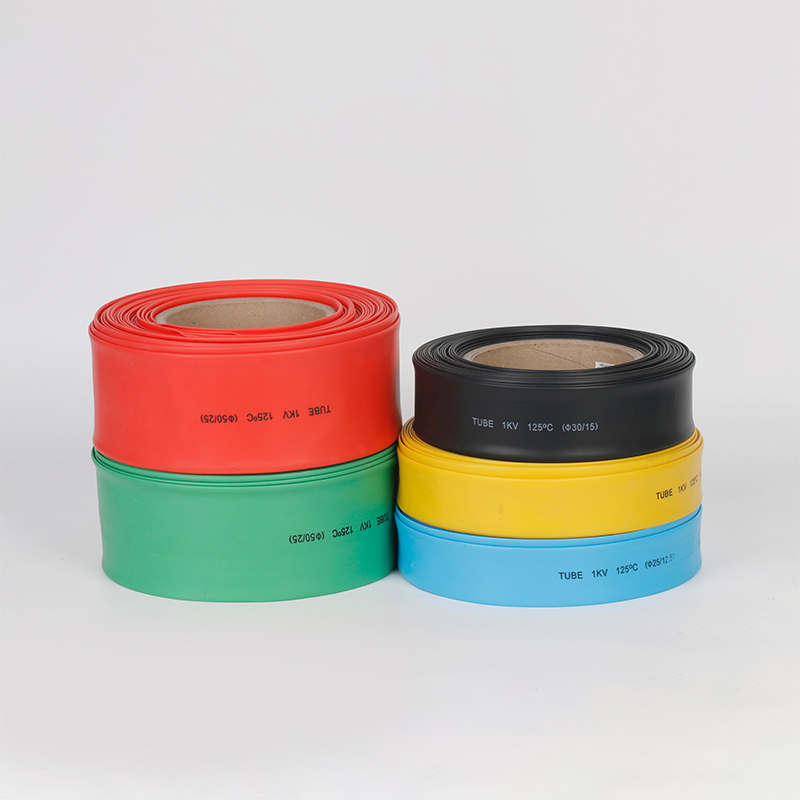
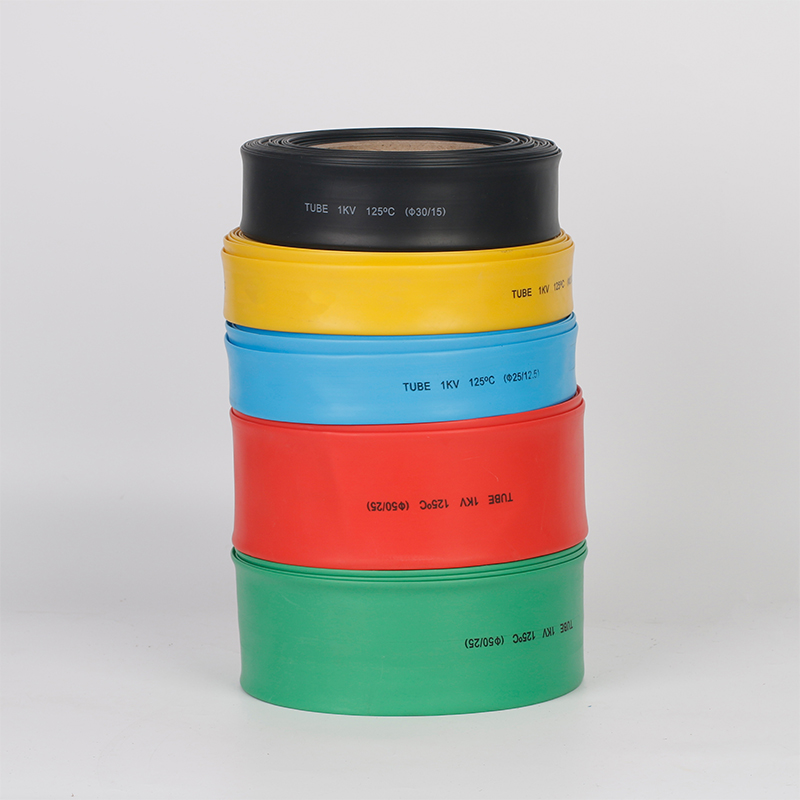
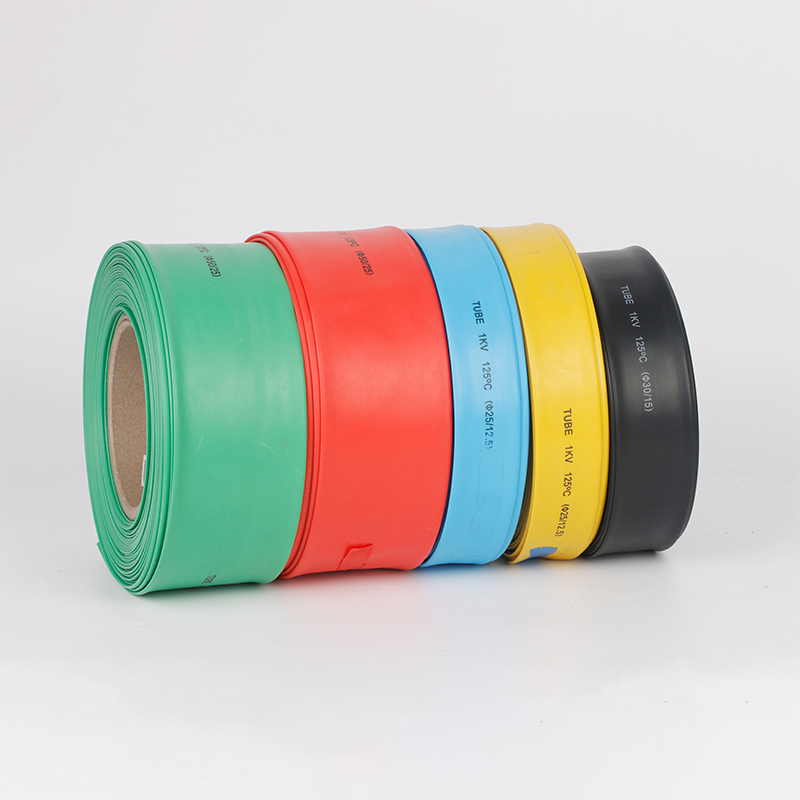
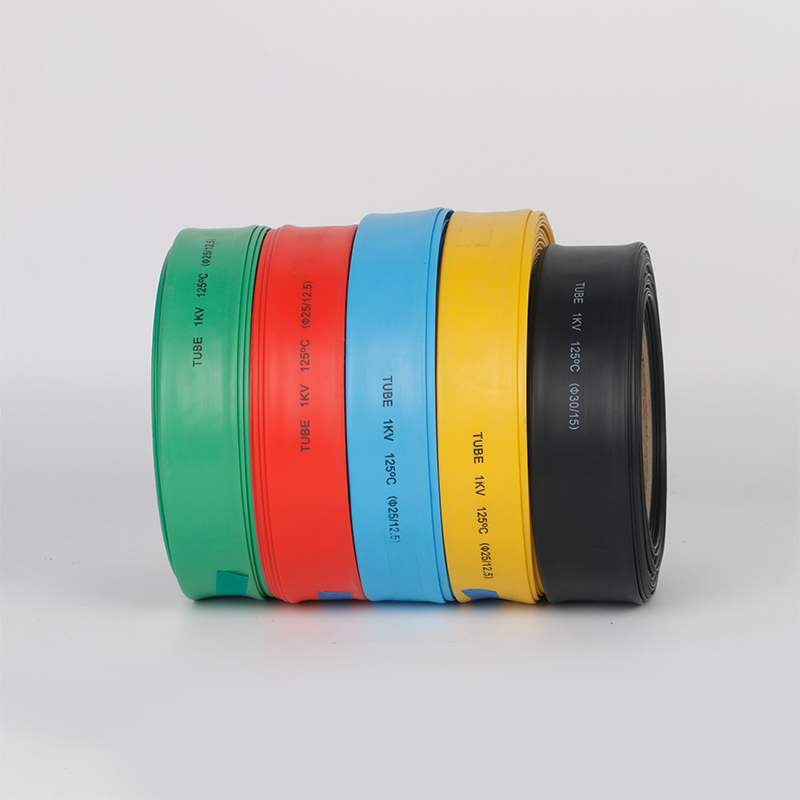
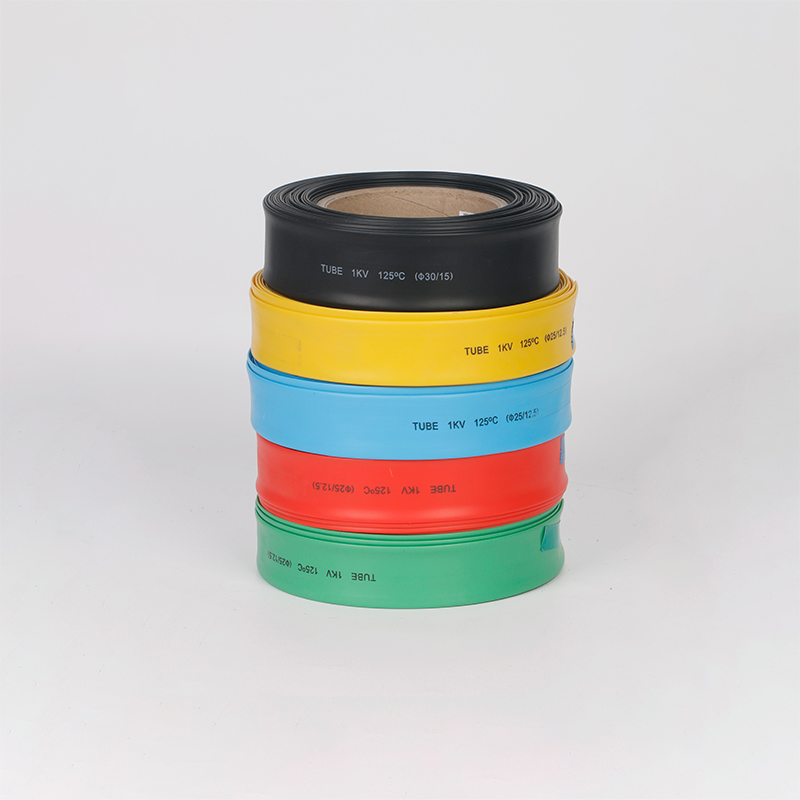
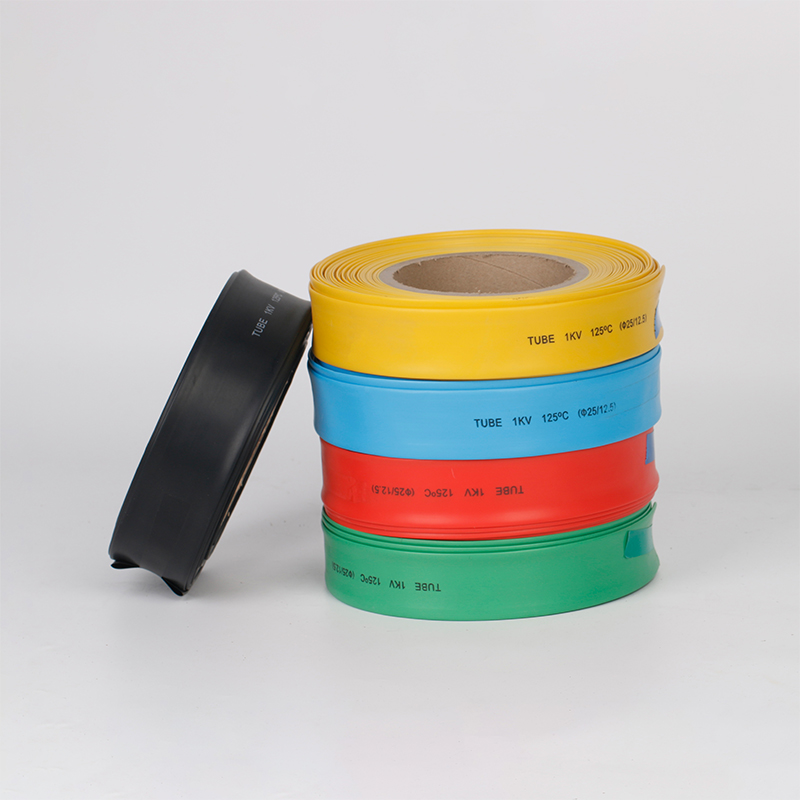
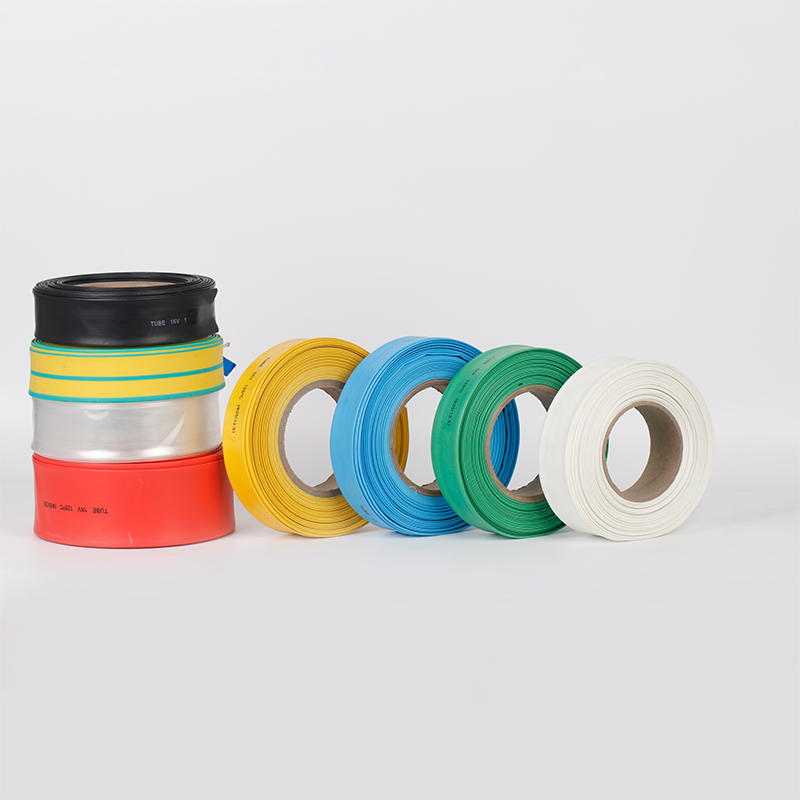
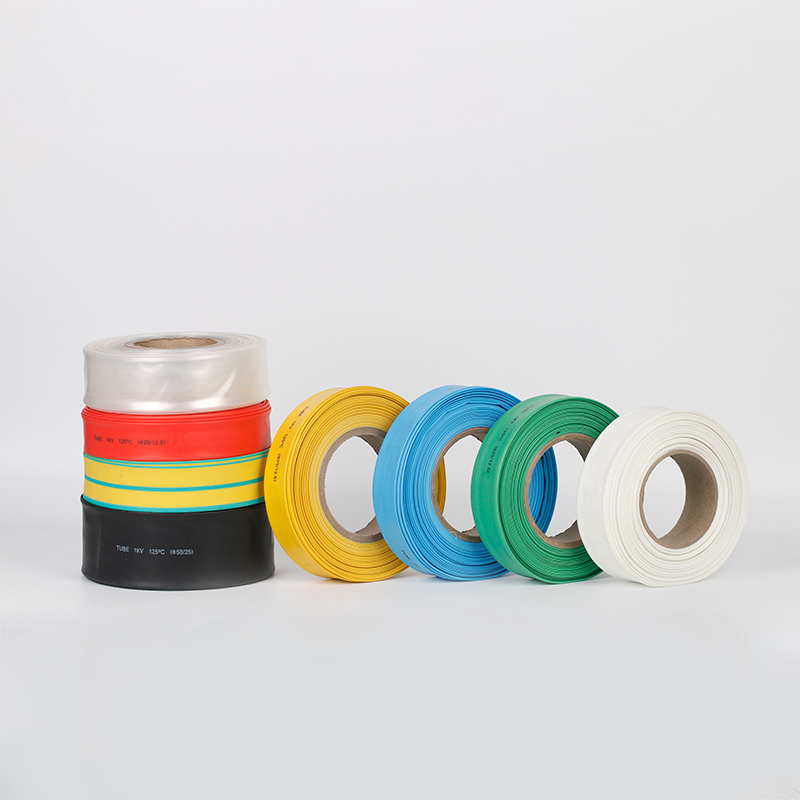
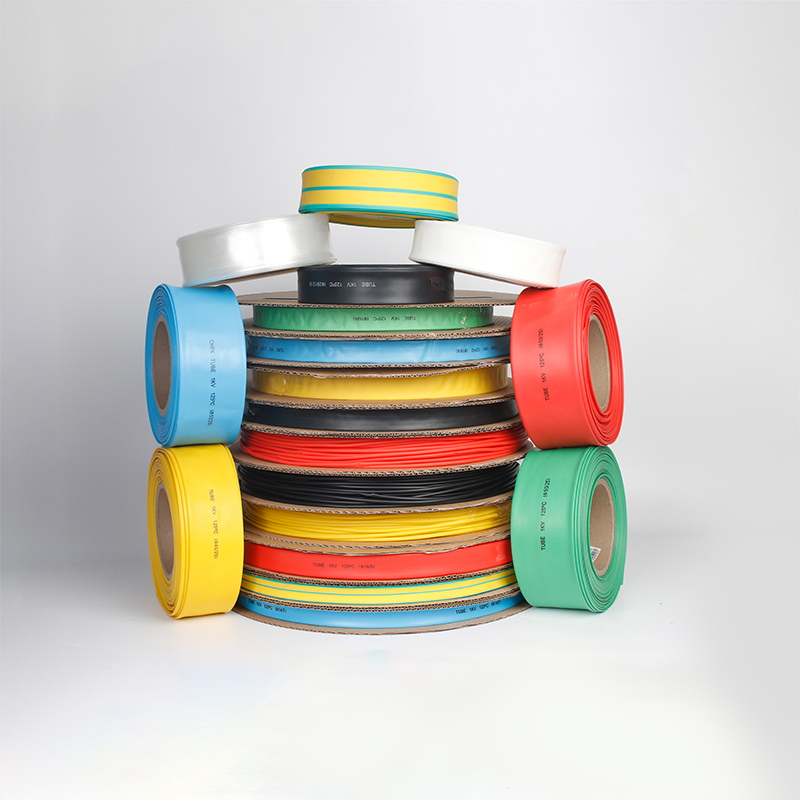
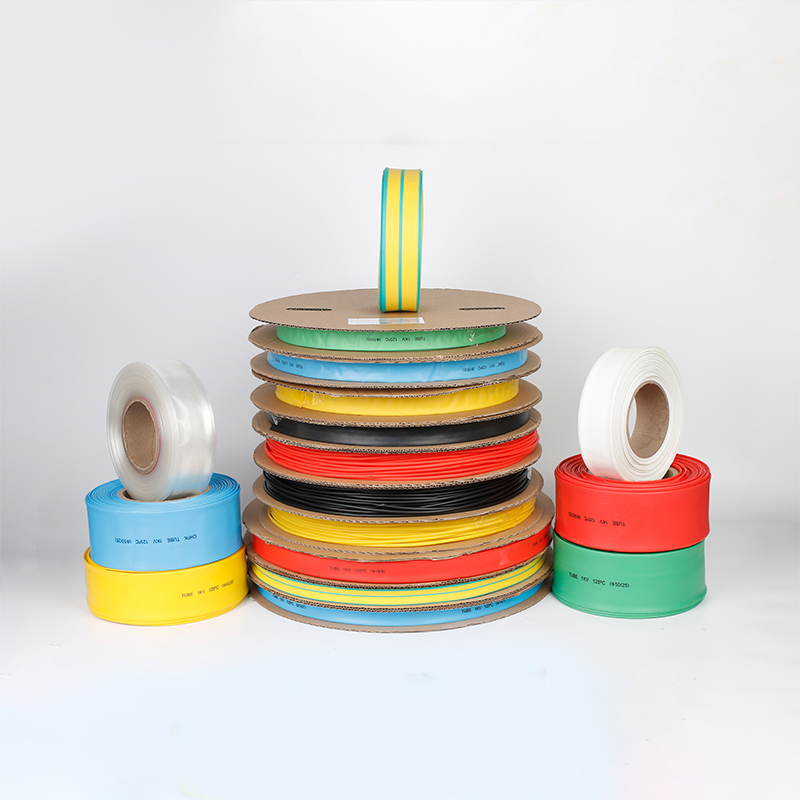
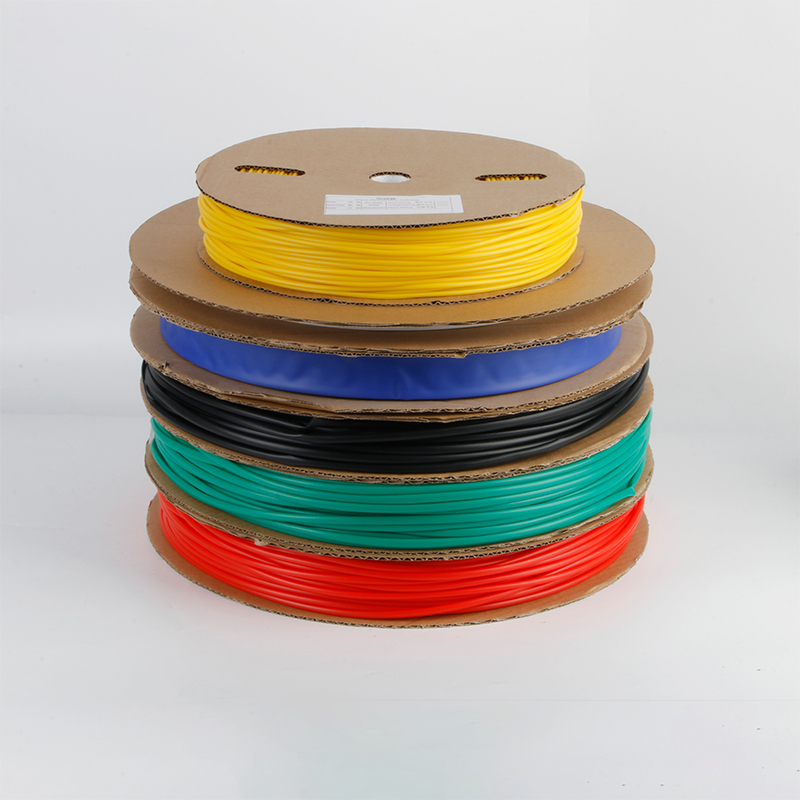
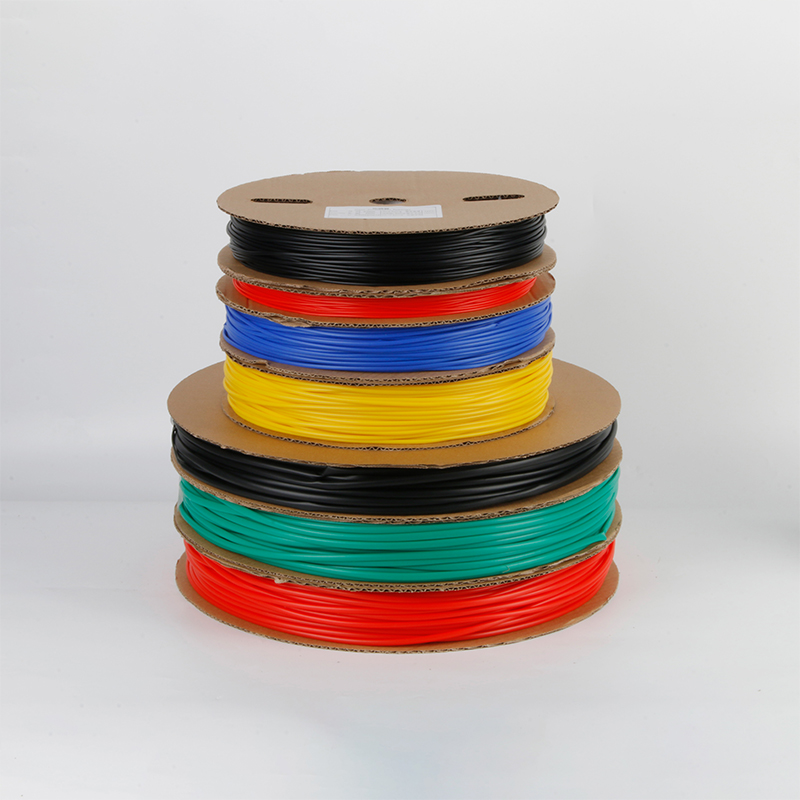
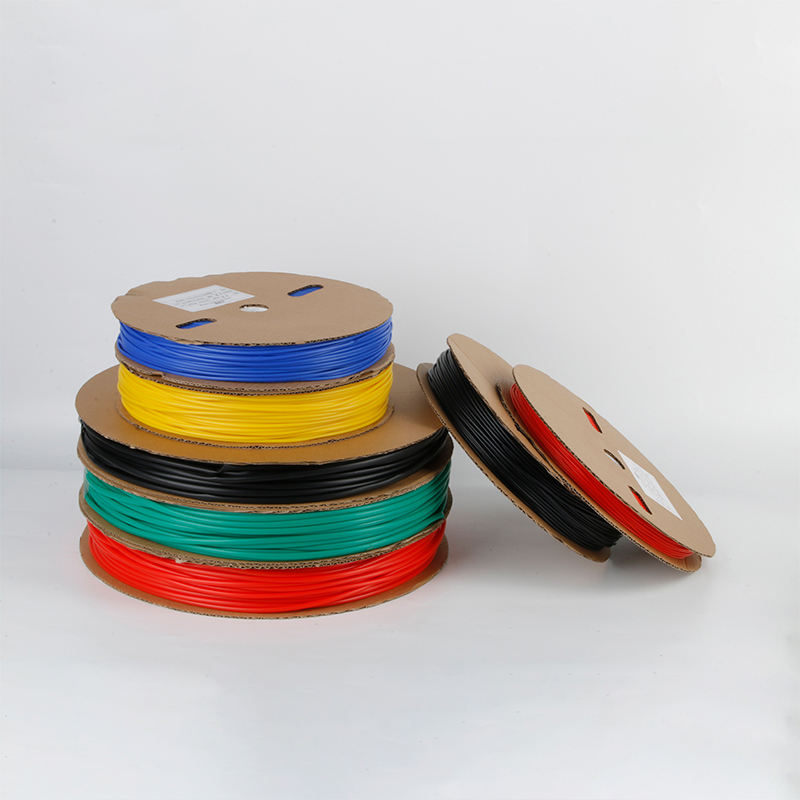
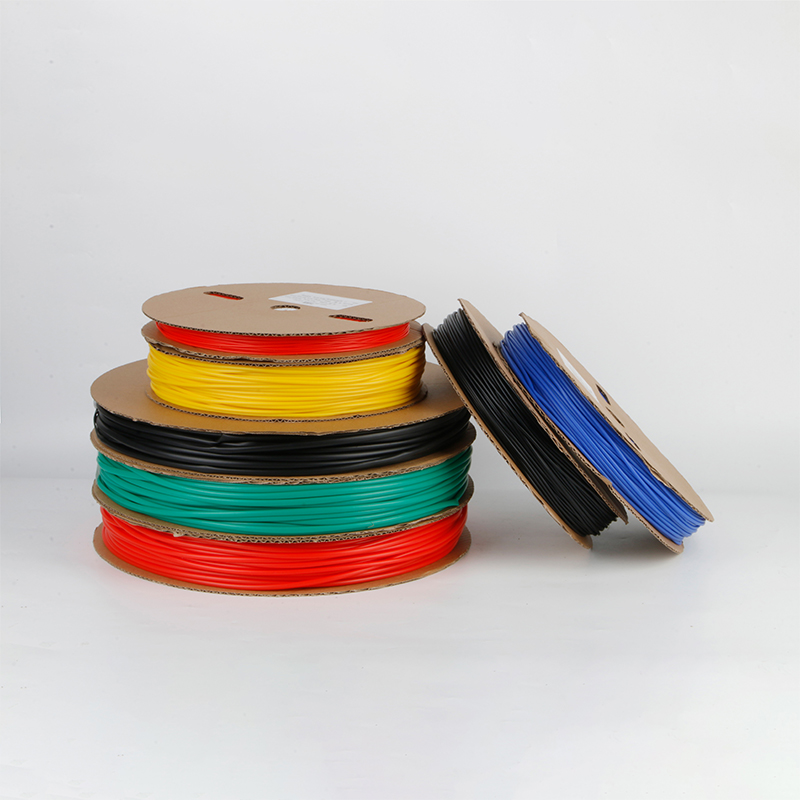
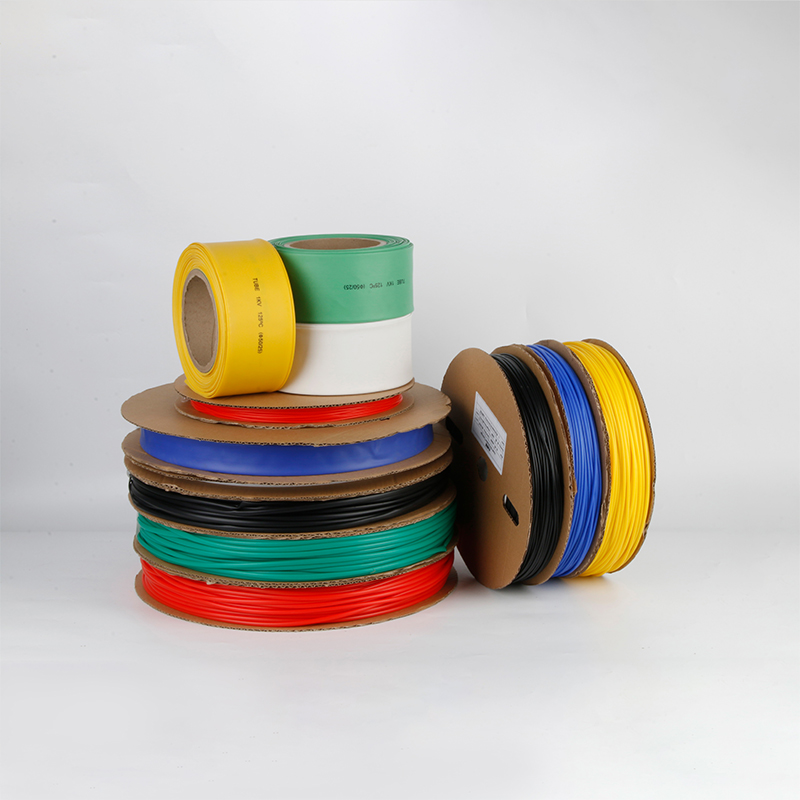
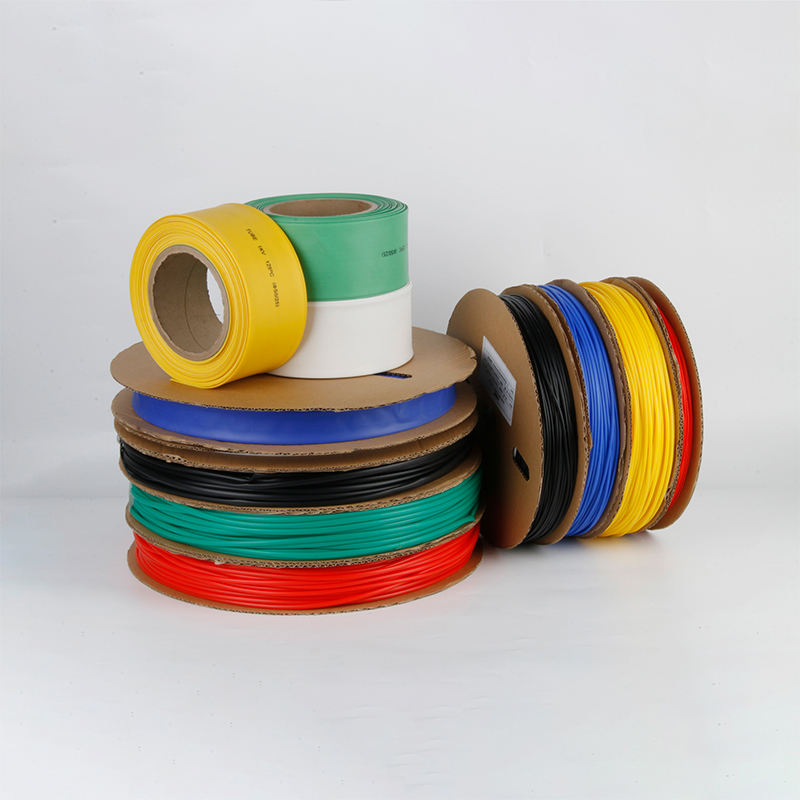
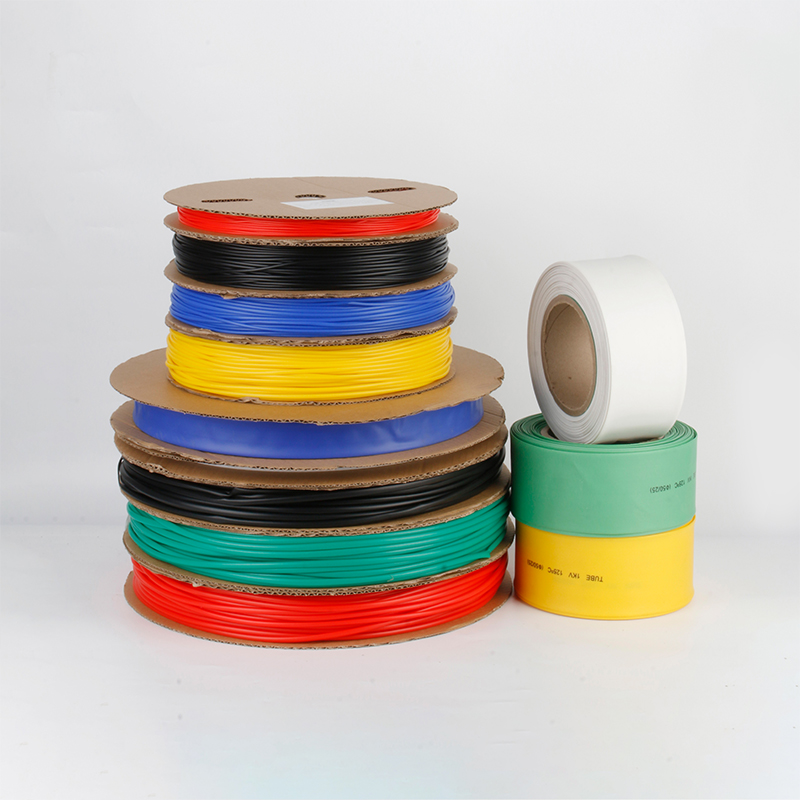
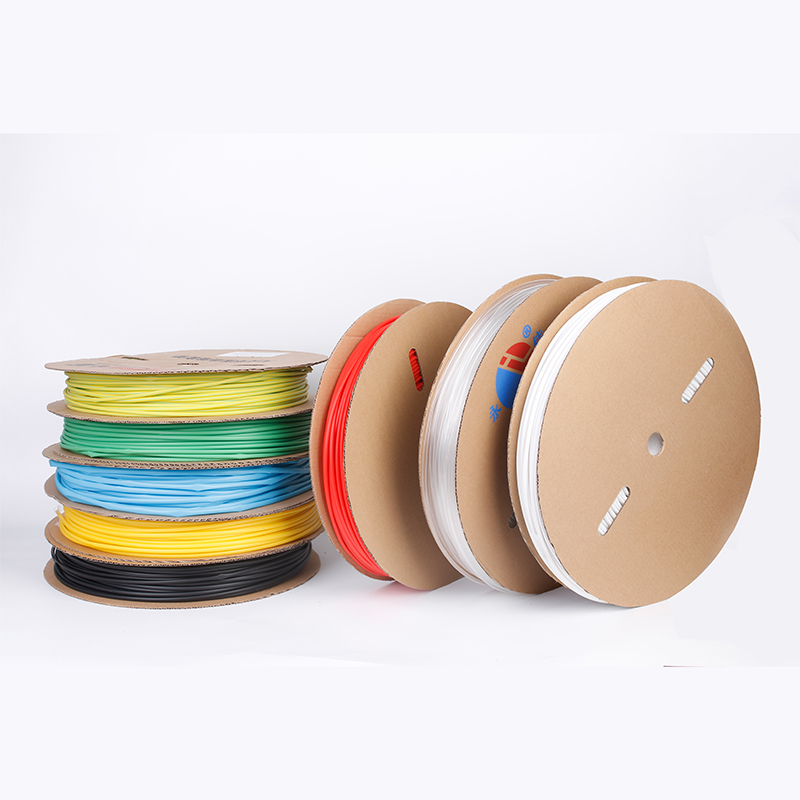
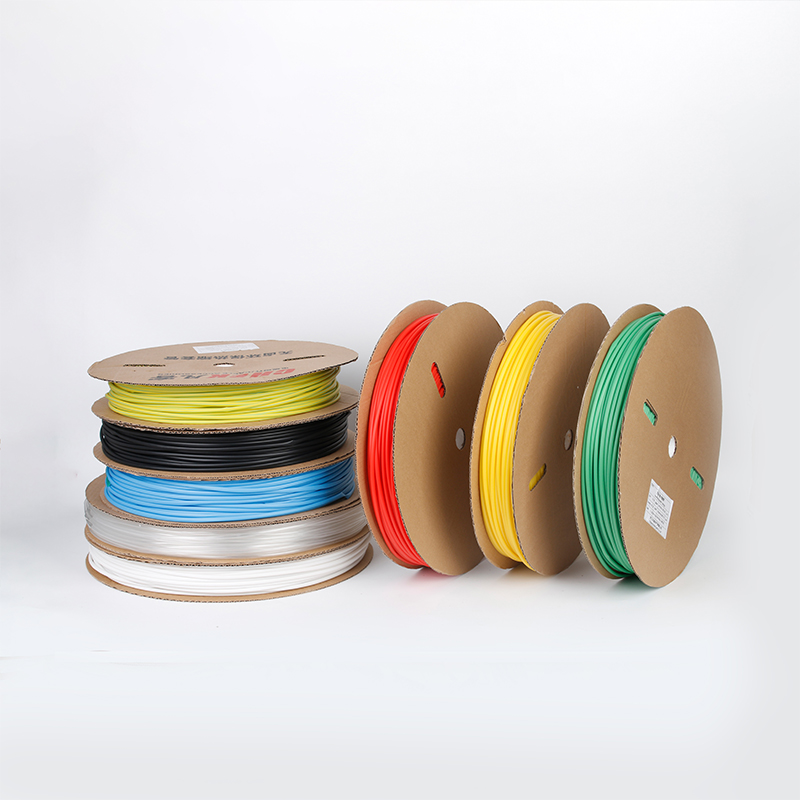
| Material | PE/ Polyolefin |
| Operation temperafure |
-55 ~125°C |
| Wire coat and insulation, divide the colors to make the joint of the terminal block, and wire insulated protection, and insulated electrical capacitors. |
|
| Function | |
| Yellow, black, white red green, blue. White. Greenyellow ,transparant.(white. GreenyellowColor | |
| Color | Transparant min size φ2, φl8 φ20 φ22 φ25 are 50m/roll) |
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Heat Shrink Tube Factory
2:1 Heat Shrink Tube
3:1 Heat Shrink Tube With Glue
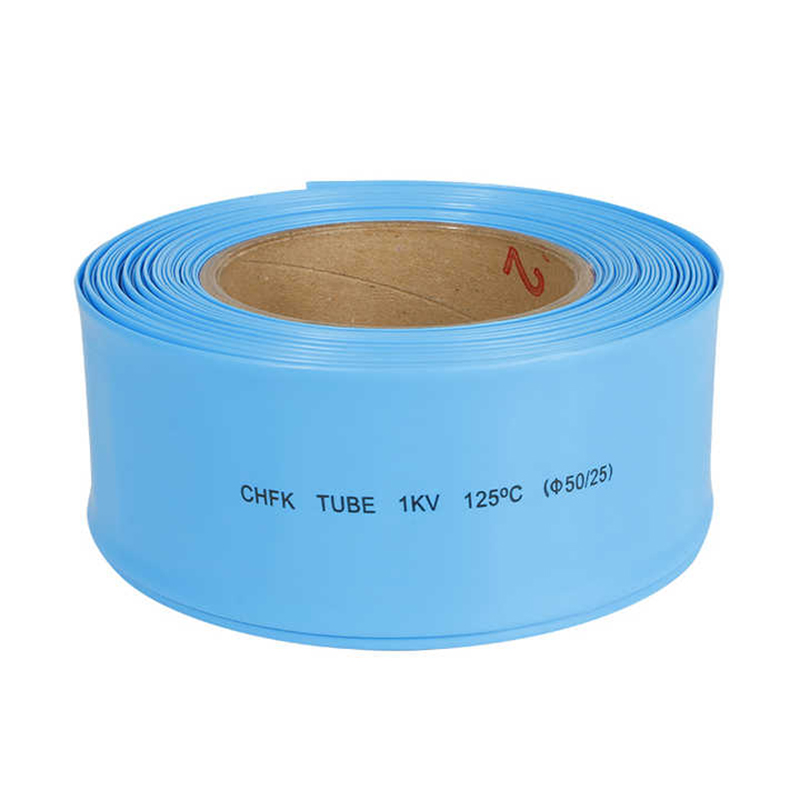
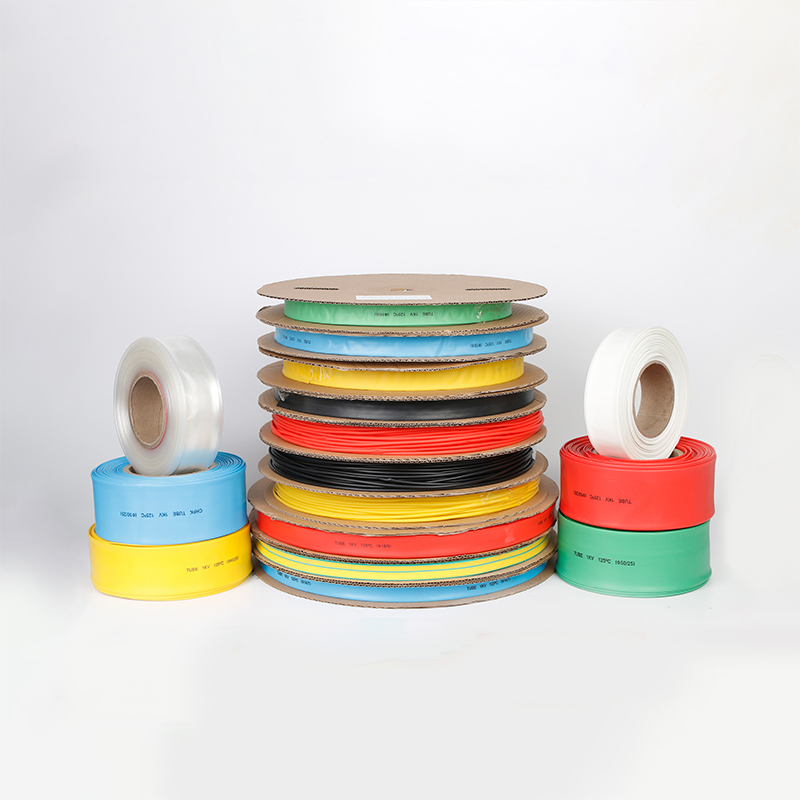
| Type | Insulation Tube |
| Material | PE |
| Application | LOWY WOLTAGE |
| Model Number | 1mm. 50mm |
| Rated voltage | 220V |
| Produce name | Dual wall heat shrink tube |
| Color |
Black.red.yellow.green.blue.transparency, |
| Size | 3OMM |
| Shrink ratio | 3:01 |
| Packing | 25 M/roll |
| Operating lemperature | 45-1259 |
| Package | Standard Package |
10KV Busbar Heat Shrink Tube
With good thermal stability, flame retardancy, softness, no cracks, and resistance to tracking, widely used in substations and switch cabinet bus bar insulation protection.
| Model | Diameter | Packaging (m) | Unit ( m ) |
| 10kV Heat shrinkable busbar |
φ25 | 50 | m |
| φ30 | 25 | m | |
| φ40 | 25 | m | |
| φ50 | 25 | m | |
| φ60 | 25 | m | |
| φ80 | 25 | m | |
| φ100 | 25 | m | |
| φ120 | 25 | m | |
| φ150 | 25 | m |
Heat shrink tubing is a flexible, tubular sleeve made from materials such as polyolefin, fluoropolymer, or PVC, designed to shrink when heated to a specific temperature. Typically, heat shrink tubing has a 2:1 or 3:1 shrink ratio, meaning that the tube will shrink to half or one-third of its original diameter when heat is applied. The tube's expansion and contraction properties make it suitable for various sealing and insulation tasks, especially in environments where durability and performance are essential.
1. Materials Used in Heat Shrink Tubing
The material choice for heat shrink tubing is crucial for its effectiveness in different environments and applications. Commonly used materials include:
Polyolefin: This is the most common material for heat-shrink tubing, offering good insulation, resistance to moisture, and flexibility. Polyolefin is widely used in electrical applications.
Fluoropolymers: These materials, such as PTFE (Teflon), offer excellent chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and low friction. Fluoropolymer-based heat shrink tubes are ideal for harsh and extreme conditions.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): PVC heat shrink tubing is known for its low cost and moderate chemical resistance, but it is generally less flexible and not as temperature-resistant as polyolefin or fluoropolymers.
Rubber: Rubber heat shrink tubes offer excellent mechanical protection and sealing, particularly in industrial and military applications.
2. Key Features of Heat Shrink Tubing
Shrink Ratio: The shrink ratio is one of the most important characteristics of heat shrink tubing. A 2:1 ratio means that the tubing will shrink to half of its original size, while a 3:1 ratio allows for more versatility, shrinking to one-third of its original size. This feature ensures that the tubing can fit snugly over a range of sizes and shapes.
Shrink Temperature: Heat shrink tubing typically shrinks at temperatures between 120°C and 200°C, depending on the material. It is essential to choose the correct tubing for the temperature range of the application.
Adhesive Lining: Some heat shrink tubes have an inner adhesive layer that melts and bonds to the surface when heated, providing an extra layer of protection. This type of tubing is often used for water resistance and sealing purposes, especially in marine or outdoor applications.
Flexibility: Heat shrink tubing is highly flexible, allowing it to conform to different shapes and sizes of objects. This property makes it particularly useful in applications where the components being covered may have irregular shapes or movements.
Durability: Heat shrink tubing is resistant to a variety of environmental factors, including moisture, UV light, dust, abrasion, and chemicals. This makes it an ideal solution for outdoor or industrial environments where cables and wires are exposed to harsh conditions.
Improved Aesthetic Appearance: Heat shrink tubing provides a sleek and professional look to wiring systems. Covering wires and cables gives installations a clean, finished appearance.
Heat shrink tubing is a highly reliable and cost-effective solution for protecting, insulating, and organizing wires and cables. Its versatility, ease of use, and durable properties make it indispensable in various industries, including electrical, automotive, aerospace, telecommunications, and marine applications. With its ability to shrink to fit different shapes and sizes, as well as its resistance to a wide range of environmental factors, heat shrink tubing remains an essential component for any project requiring reliable cable protection.

About Us
Honor
-
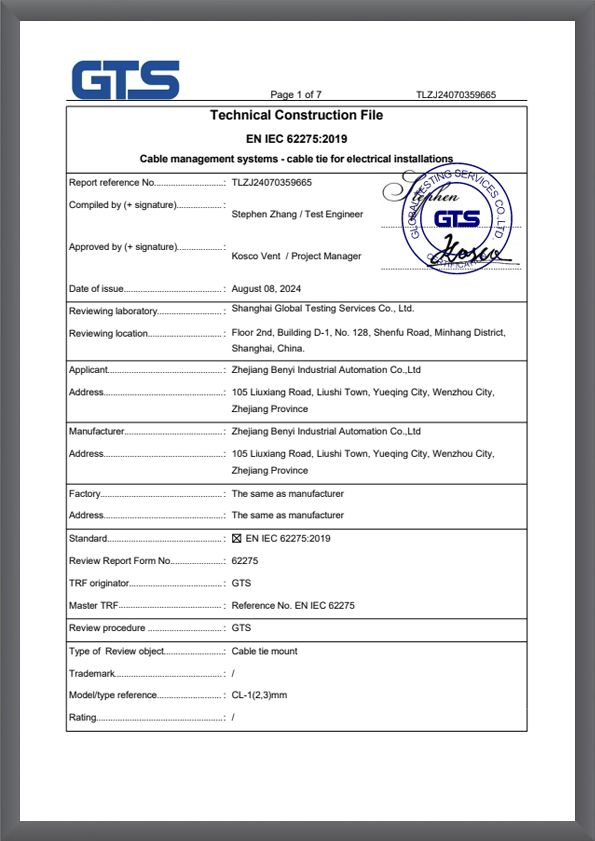 TLZJ24070359665
TLZJ24070359665 -
 CLZJ24070359665
CLZJ24070359665 -
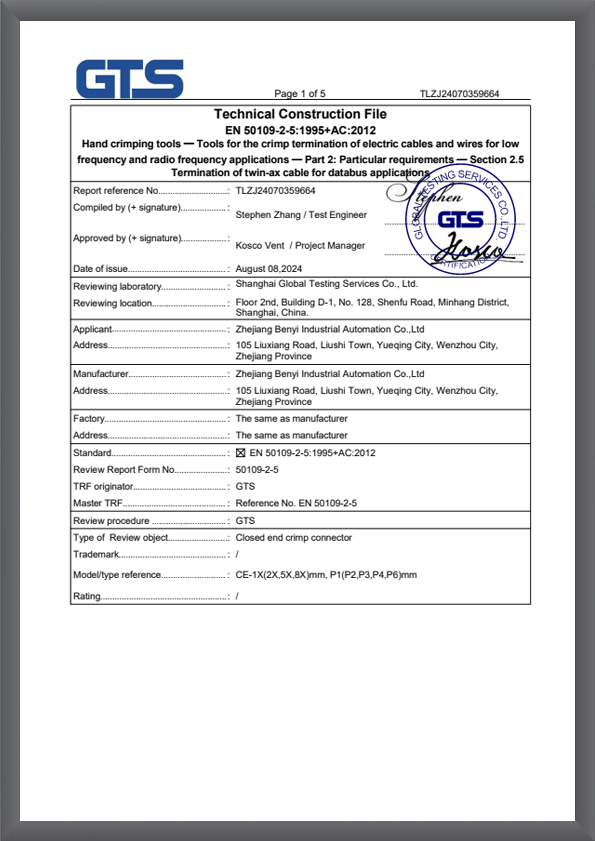 TLZJ24070359664
TLZJ24070359664 -
 CLZJ24070359664
CLZJ24070359664 -
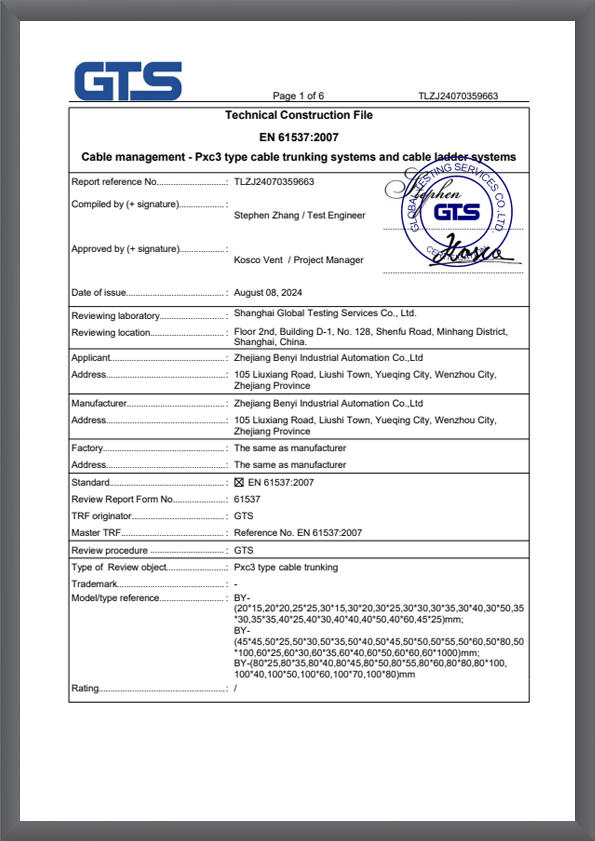 TLZJ24070359663
TLZJ24070359663 -
 CLZJ24070359663
CLZJ24070359663
News
-
Industry News 2026-02-13
Copper terminals and lugs are common components in electrical distribution and wiring systems, serving both conductivity and mechanical connection pur...
View More -
Industry News 2026-02-06
Cold-pressed insulated terminals are widely used in electrical systems to provide secure and reliable wire connections. These terminals are manufactur...
View More -
Industry News 2026-01-30
2:1 heat shrink tubes are widely used in industrial and electronic applications due to their ability to provide electrical insulation, mechanical prot...
View More -
Industry News 2026-01-23
Brass cable glands are essential components in industrial electrical systems. They secure cables as they enter equipment or enclosures, providing stra...
View More
Contact us now

 +86-15558905711
+86-15558905711 +86-15057372736
+86-15057372736 [email protected]
[email protected] 105 Liuxiang Road, Liushi Town, Yueqing City, Wenzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
105 Liuxiang Road, Liushi Town, Yueqing City, Wenzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
 英语
英语 中文简体
中文简体 俄语
俄语 西班牙语
西班牙语









































