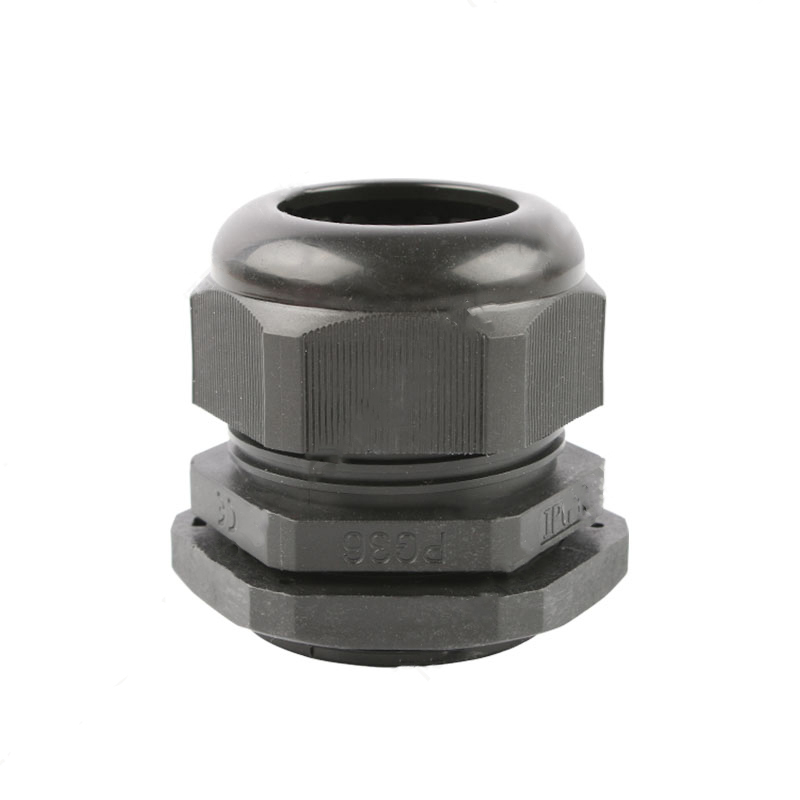
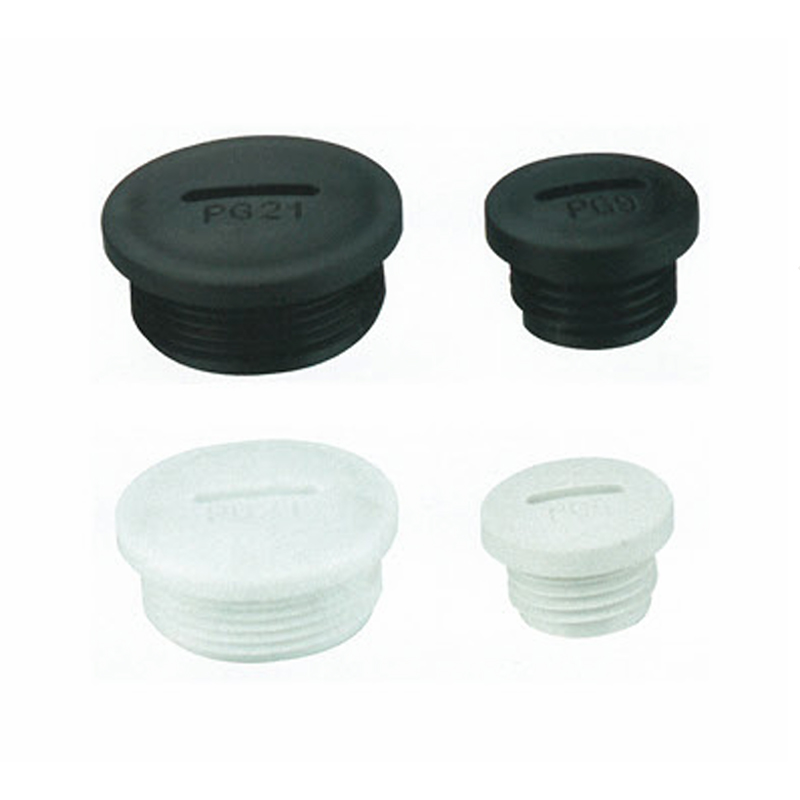
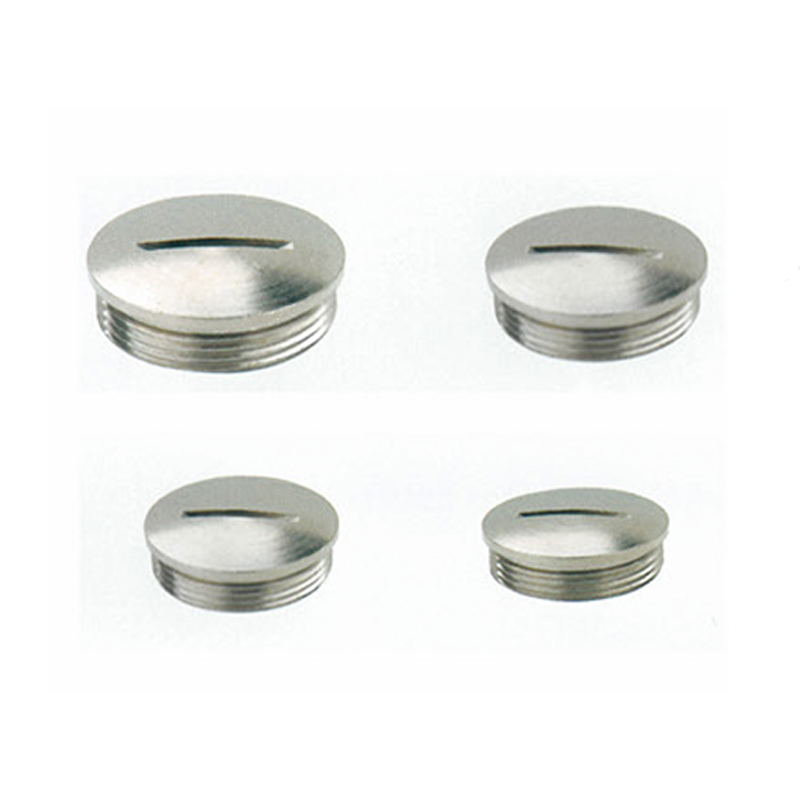
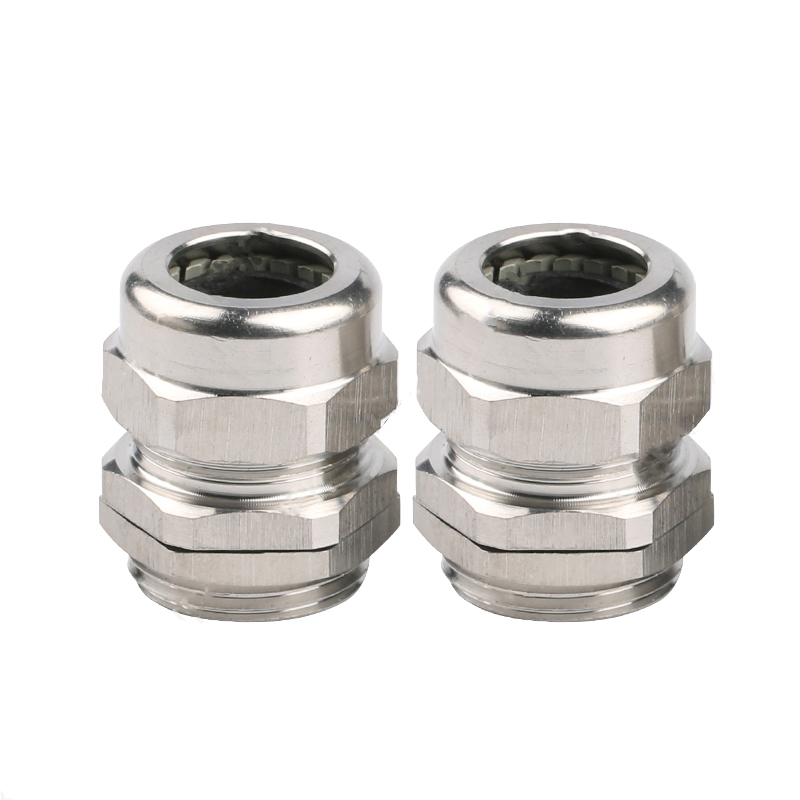
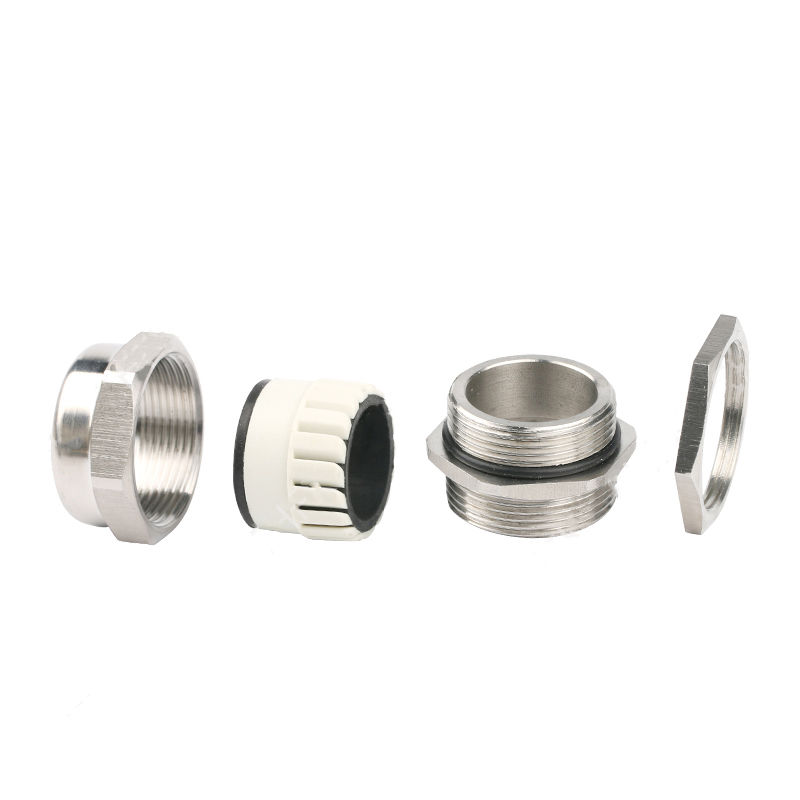
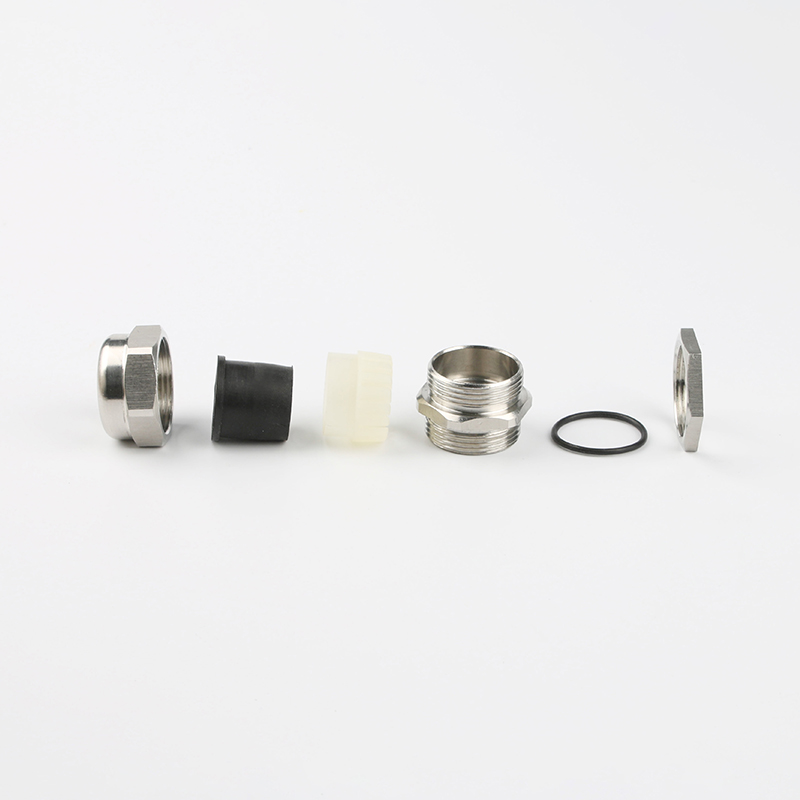
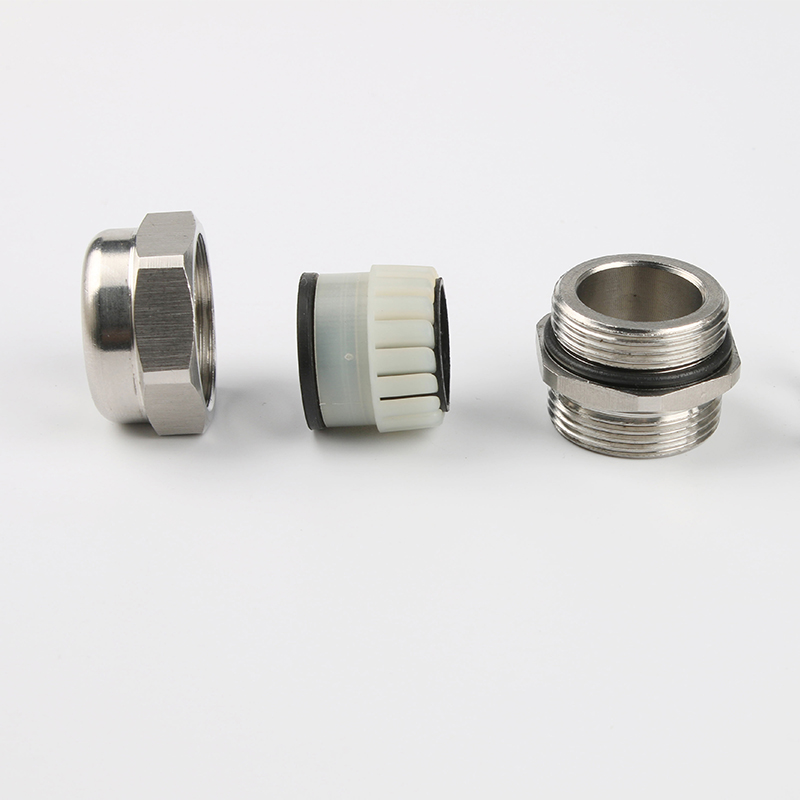
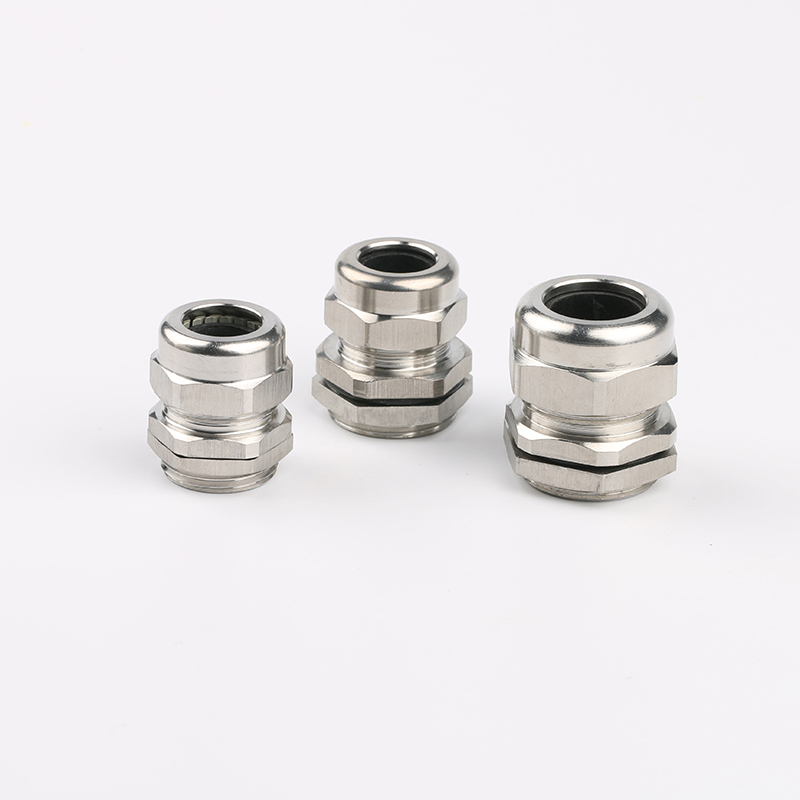
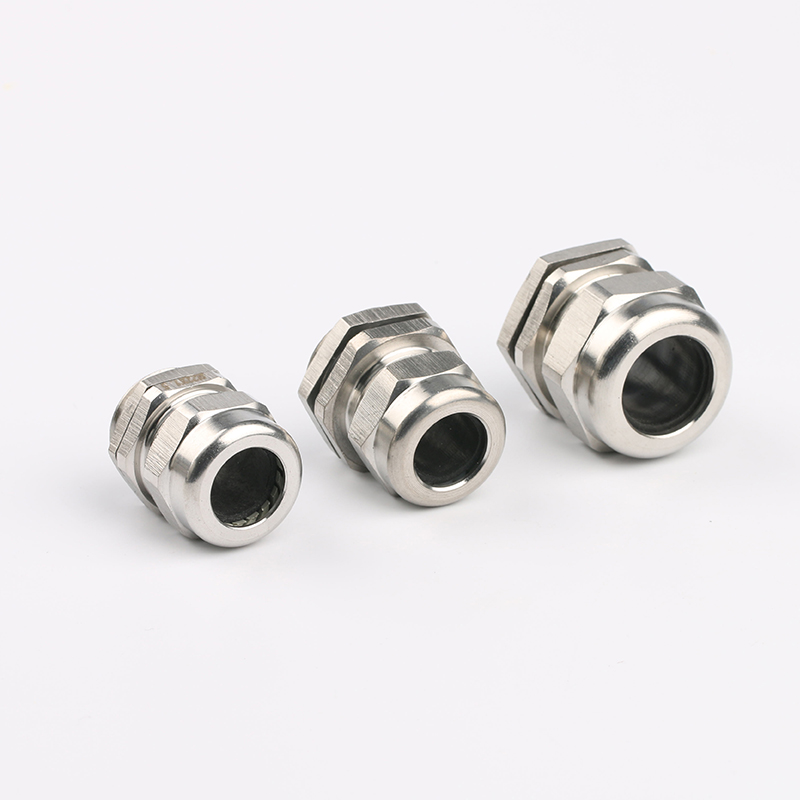
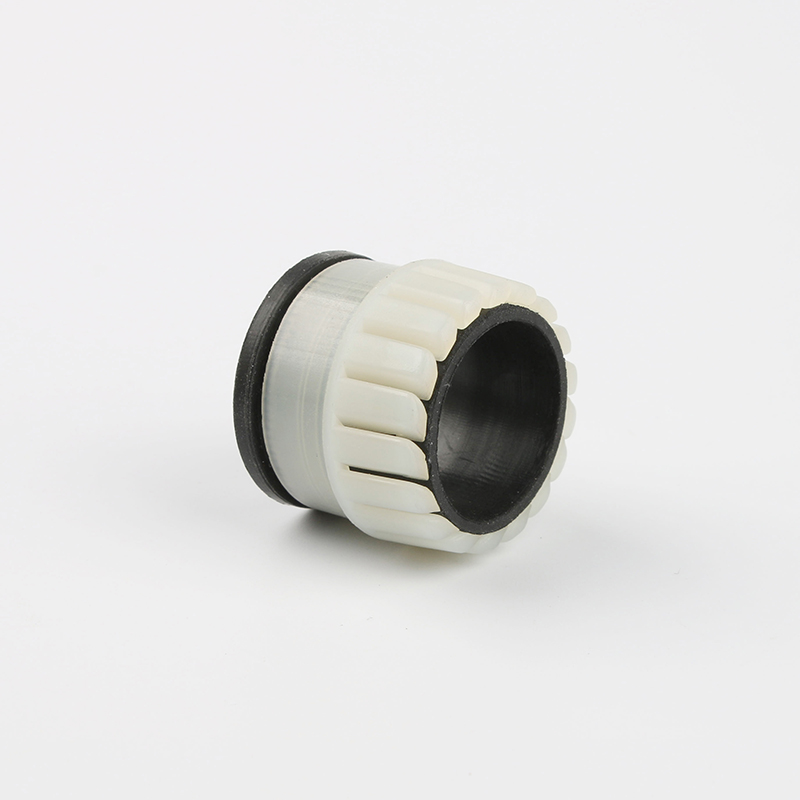
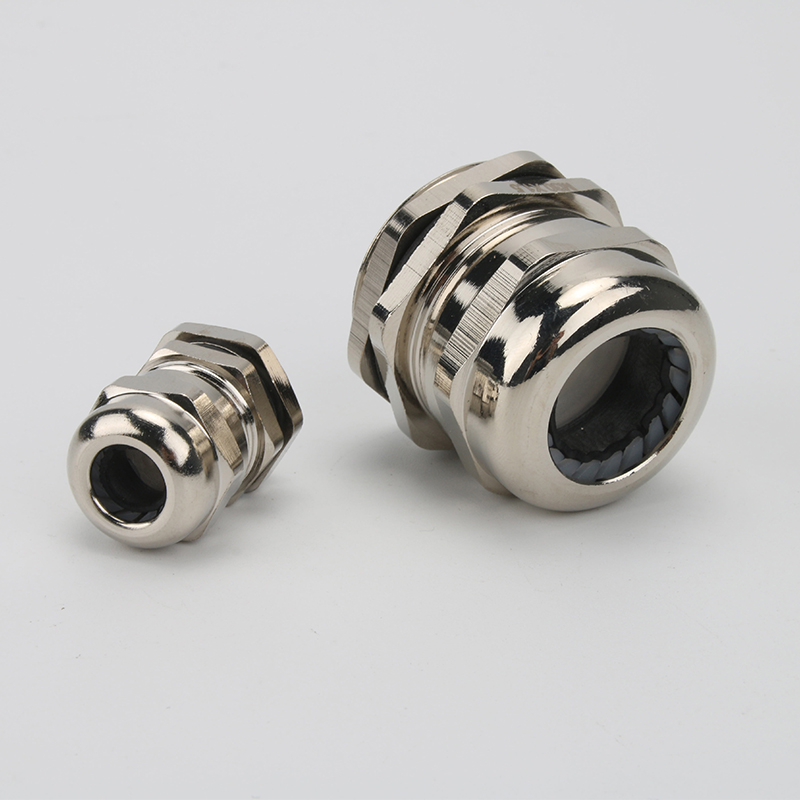
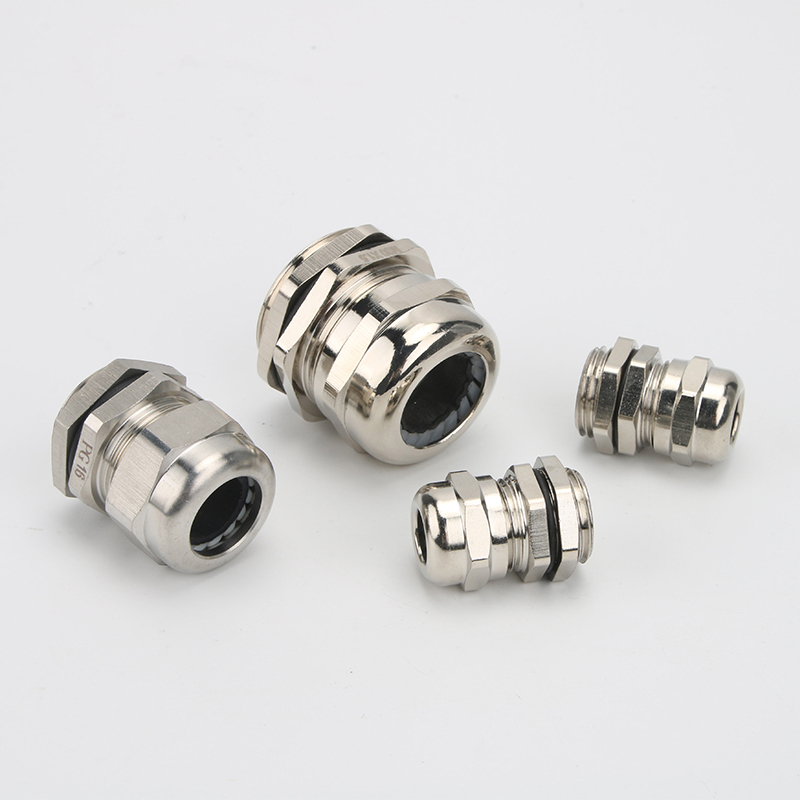
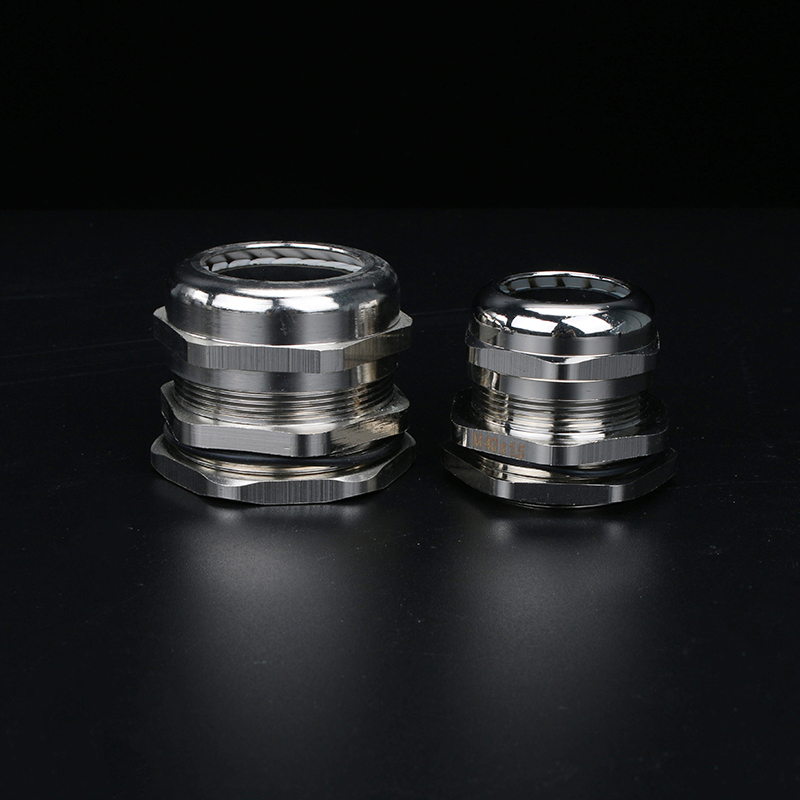
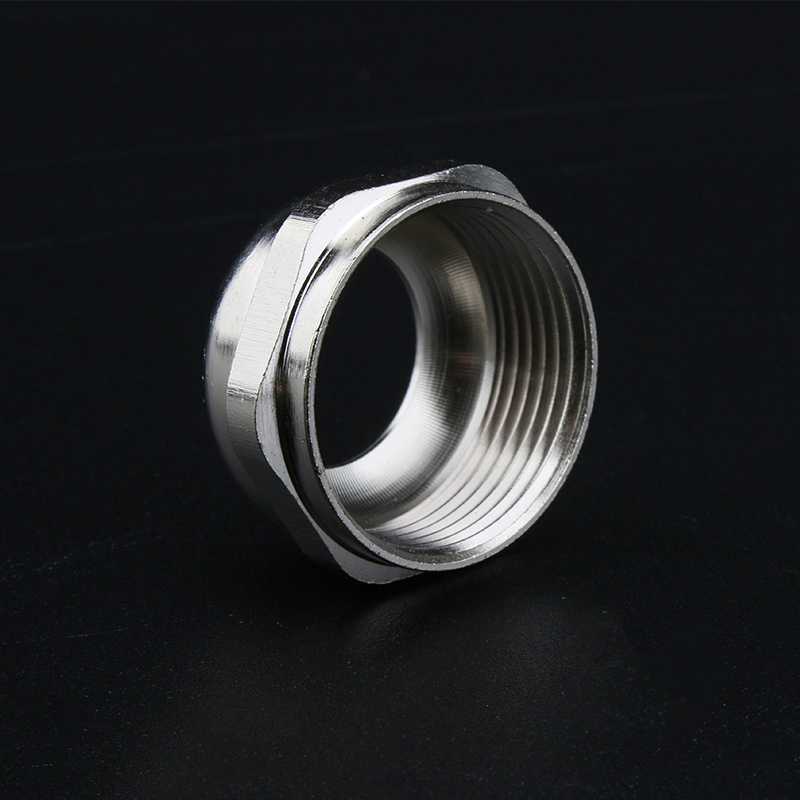
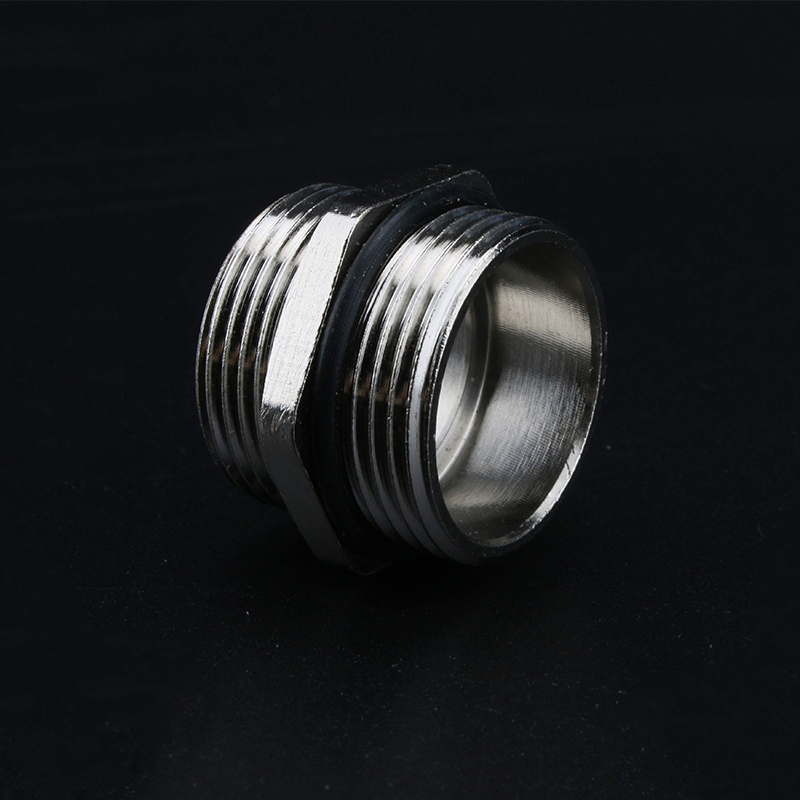
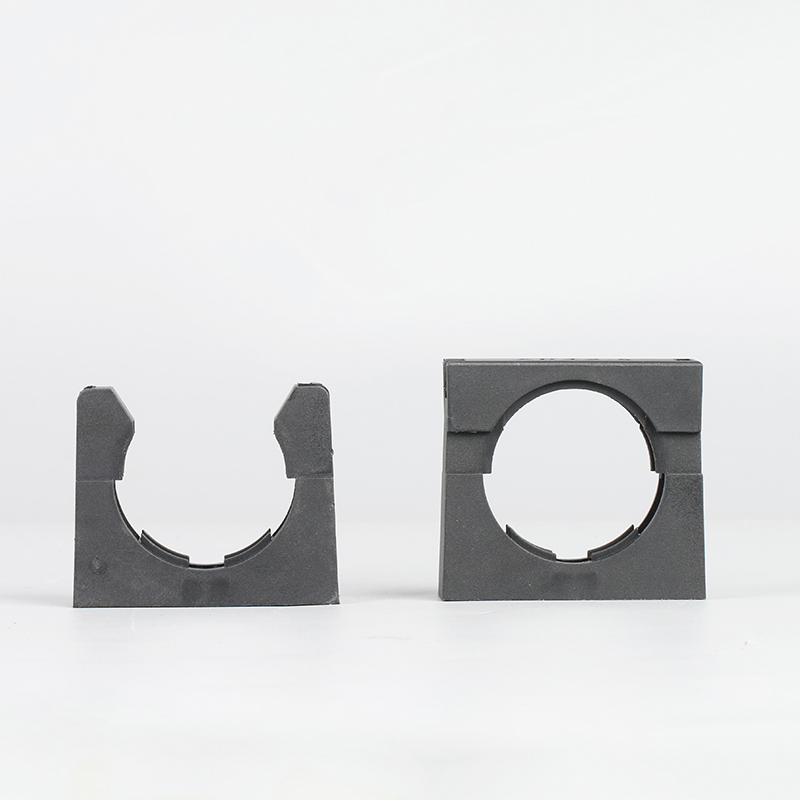
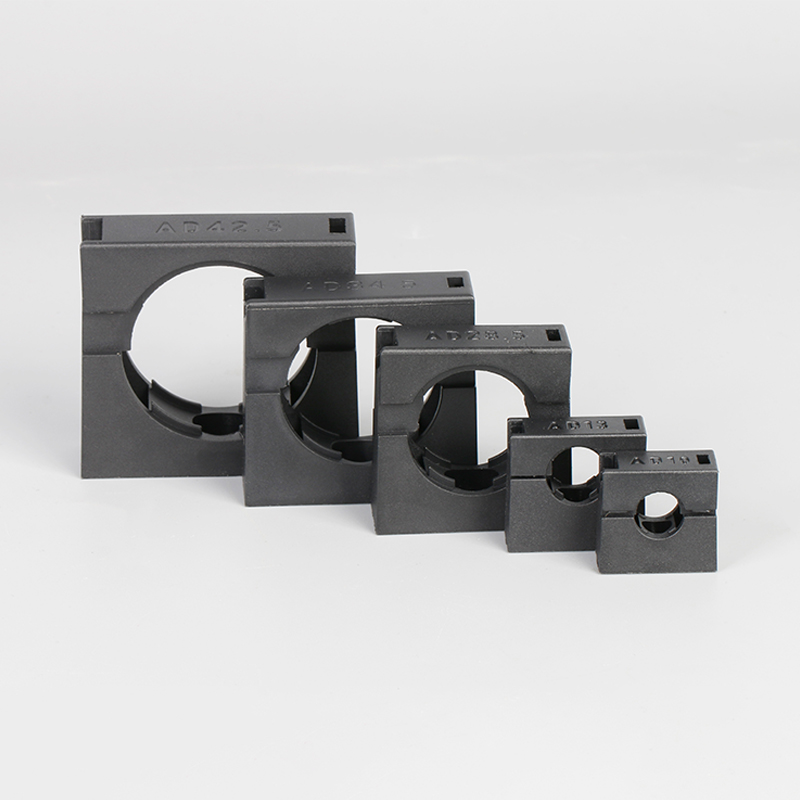
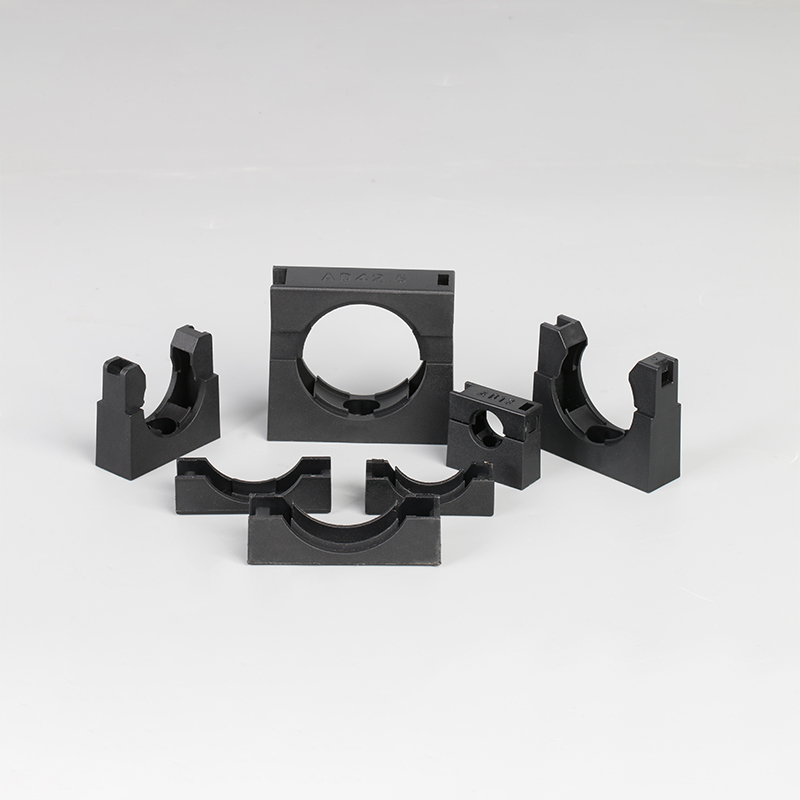
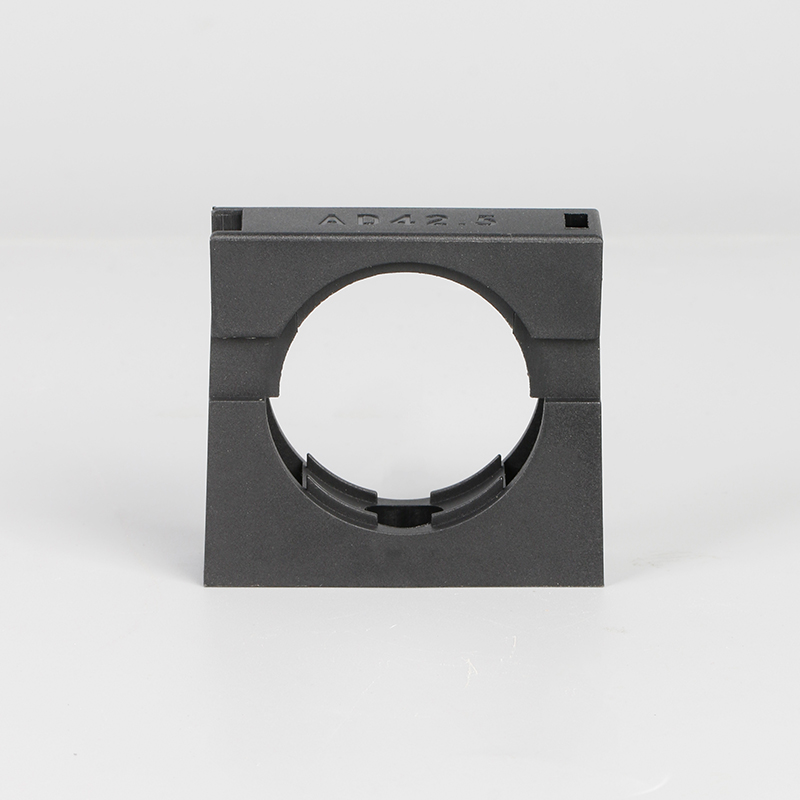
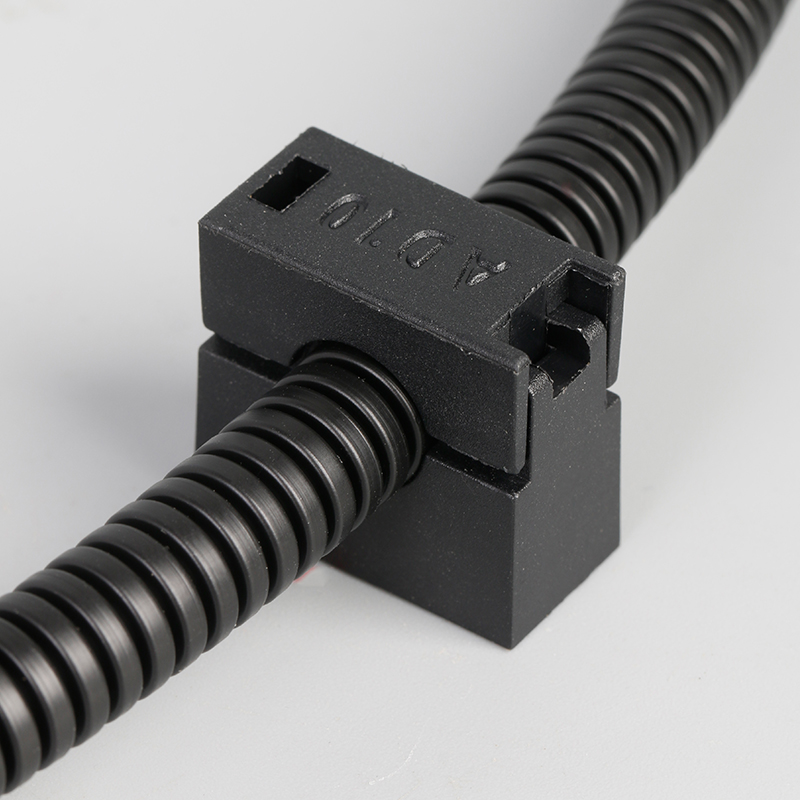
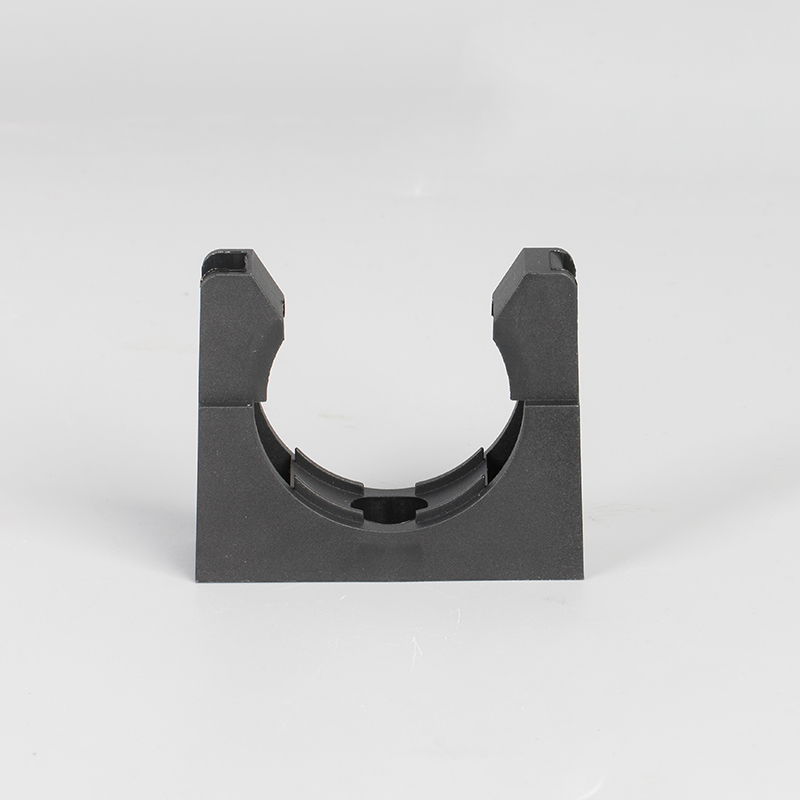
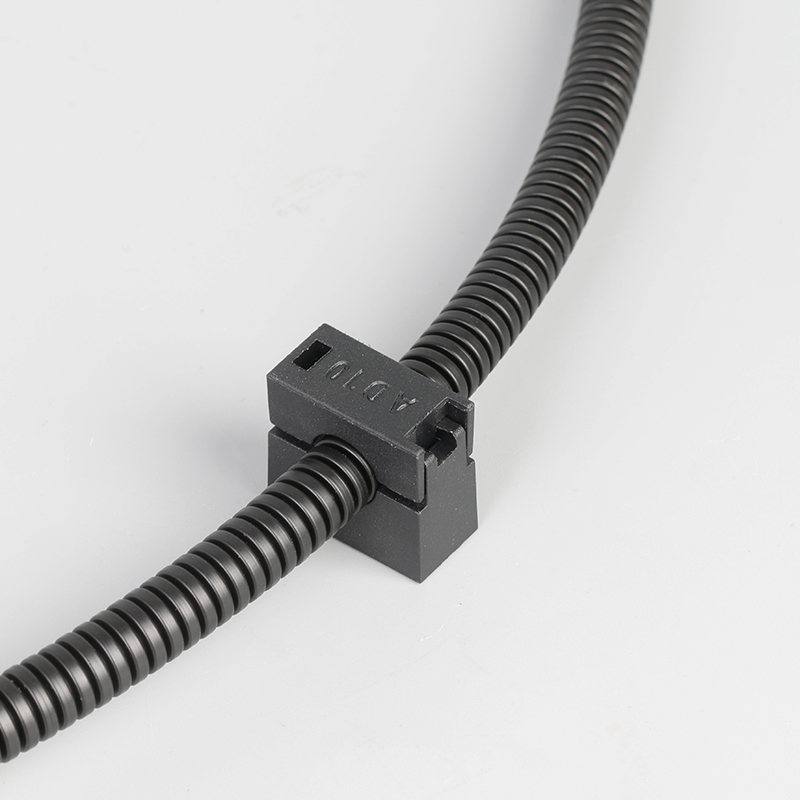
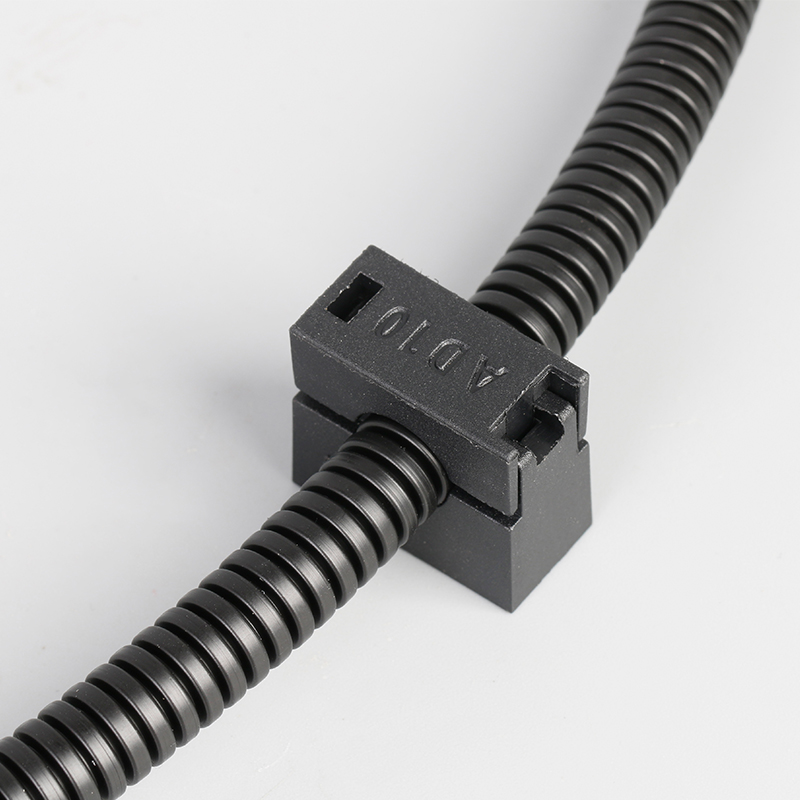
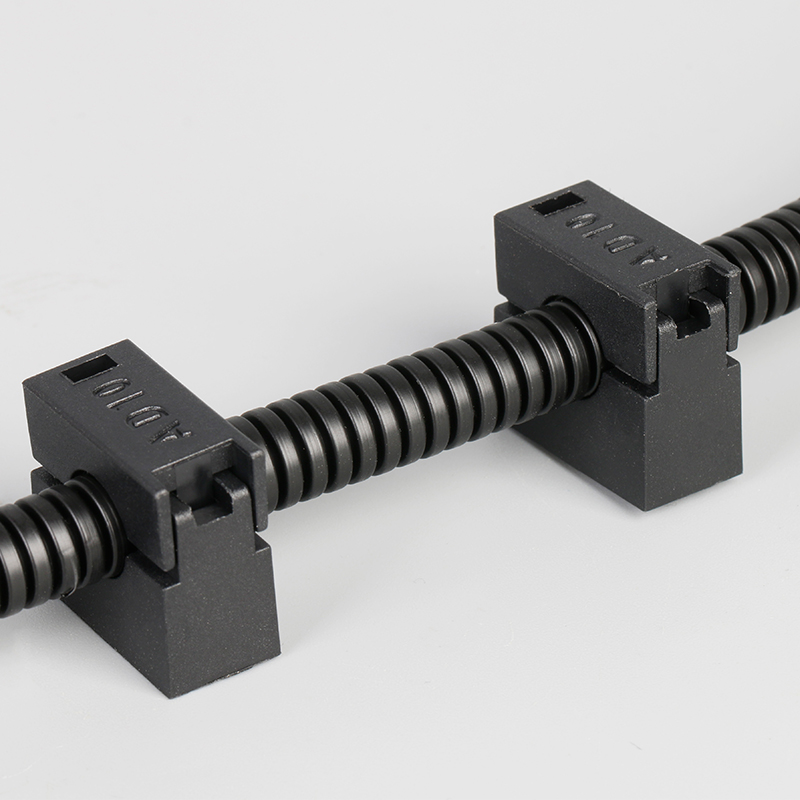
A Cable Gland is a device used to secure and protect the ends of electrical cables as they enter an enclosure or piece of electrical equipment. Typically made from materials like brass, stainless steel, or plastic, cable glands are crucial in ensuring the safety and durability of electrical systems by preventing cable damage and sealing the entry points against dust, water, and other environmental factors. The use of cable glands is widespread in various industries, including electrical, telecommunications, and automation.
1. Primary Function of Cable Glands
Cable glands serve two primary functions:
Mechanical Strain Relief: They provide mechanical support by firmly holding the cable in place, preventing strain on the cable's core or connectors due to movement or vibration. This helps to prevent premature wear or damage.
Sealing and Environmental Protection: Cable glands create a tight seal around the cable, protecting it from contaminants such as dust, moisture, and chemicals. This sealing feature is particularly important for systems operating in harsh environments, ensuring the longevity of both the cable and the connected electrical equipment.
2. Materials Used in Cable Glands
Cable glands come in various materials, each offering distinct advantages depending on the application:
Brass Cable Glands: Brass is one of the most commonly used materials due to its excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and good electrical conductivity. Brass glands are ideal for general applications in environments that are not extremely corrosive.
Stainless Steel Cable Glands: Stainless steel is used in more demanding environments, particularly in industries that require enhanced corrosion resistance, such as marine and chemical processing. Stainless steel glands are robust and can withstand exposure to harsh chemicals, high temperatures, and salty air.
Plastic Cable Glands: For lighter-duty applications, plastic cable glands are used. They are resistant to corrosion, light in weight, and cost-effective. These glands are ideal for indoor or less demanding outdoor environments.
3. Features of Cable Glands
Ingress Protection (IP Rating): Cable glands are often rated by their IP rating, which indicates their ability to protect against dust and water ingress. A high IP rating (e.g., IP68) means the gland can provide a high level of protection in harsh environments, including complete water immersion.
Temperature Resistance: Many cable glands are rated to operate within a wide temperature range. For example, they may function in environments with temperatures ranging from -40°C to 100°C, depending on the material and design.
Easy Installation and Maintenance: Most cable glands are designed for simple installation. Some glands feature a screw-on or clamp design that allows for easy cable entry without requiring specialized tools. This ease of installation helps reduce downtime in critical operations.
Vibration Resistance: Cable glands can be designed to resist vibrations, which is essential in industrial machinery, automotive applications, and other high-movement environments. This feature ensures the cable remains securely attached and properly sealed.
4. Choosing the Right Cable Gland
When selecting a cable gland, several factors should be considered:
Cable Size and Type: The gland should be compatible with the specific cable size and type to ensure proper sealing and strain relief.
Environment: Consider environmental factors such as exposure to moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures. Choose glands with the appropriate IP rating and material for the environment.
Certifications: For industries with strict regulations, ensure the chosen gland meets necessary standards such as IECEx, ATEX, or UL certifications.
 英语
英语 中文简体
中文简体 俄语
俄语 西班牙语
西班牙语