Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Cold-Pressed Insulated Terminals Enhancing Electrical Safety and Efficiency in 2025
Cold-Pressed Insulated Terminals have become a cornerstone in modern electrical systems, offering reliable connections and enhanced safety. In 2025, their applications have expanded across various industries, including automotive, renewable energy, industrial automation, and consumer electronics, driven by the increasing demand for efficient, secure, and long-lasting electrical connections. The consistent performance of these terminals helps reduce maintenance costs and improves overall system reliability, making them a preferred choice for engineers and manufacturers worldwide.
Cold-Pressed Insulated Terminals: A Reliable Connection Solution
Cold-pressed insulated terminals provide a secure and durable connection between wires and electrical components. The cold-pressing process ensures a strong mechanical bond without the need for heat, preserving the integrity of sensitive components. These terminals are resistant to vibration, corrosion, and thermal stress, which makes them suitable for harsh industrial and outdoor environments. Their precision-engineered design minimizes the risk of electrical faults and ensures stable current flow, contributing to safer and more efficient operations.
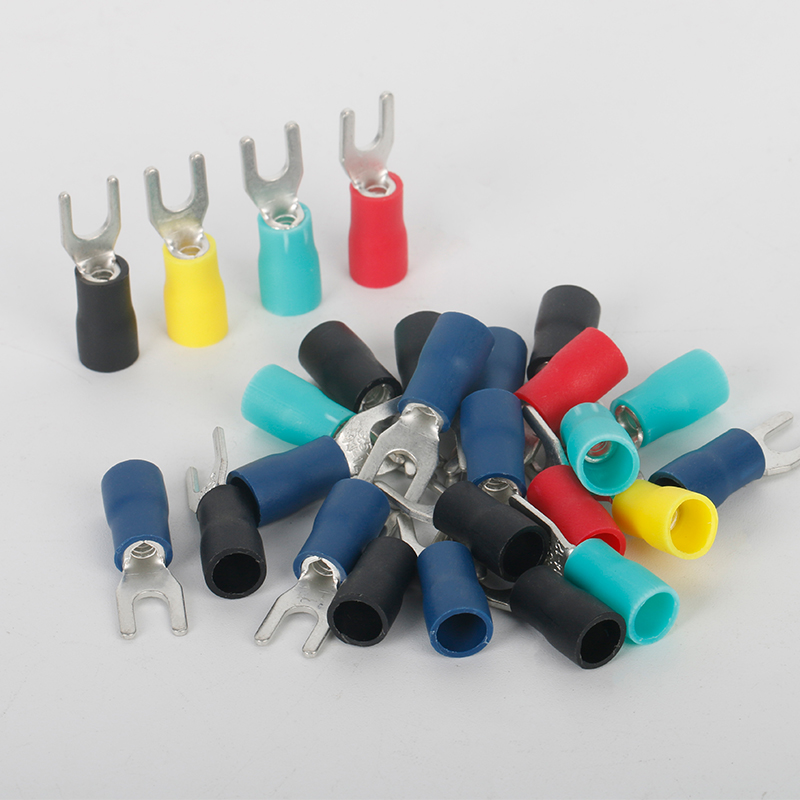

Applications in Automotive and Renewable Energy Sectors
In the automotive industry, cold-pressed insulated terminals are utilized in wiring harnesses, battery connections, sensor networks, and electric vehicle power systems. Their ability to withstand high temperatures, mechanical vibrations, and moisture ensures the reliability of electrical systems over long periods of use. In renewable energy applications, these terminals are used in solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems. Their durability under outdoor conditions, including temperature fluctuations and humidity, makes them essential for maintaining consistent energy output and safety compliance.
Advancements in Materials and Manufacturing Processes
Recent innovations in materials and manufacturing have further improved the performance of cold-pressed insulated terminals. Tin-plated copper, high-performance insulation, and eco-friendly polymers provide enhanced conductivity, corrosion resistance, and environmental sustainability. Automated production techniques and precision pressing tools enable consistent quality across large production volumes. Manufacturers are focusing on reducing material waste and improving process efficiency, ensuring terminals meet high standards while aligning with sustainability goals.
Meeting Industry Standards and Regulatory Requirements
Compliance with industry standards remains critical for cold-pressed insulated terminals. Certifications such as UL, CE, and RoHS confirm that these components meet strict electrical, mechanical, and environmental requirements. Adherence to such standards ensures that terminals maintain performance under extreme conditions, prevent safety hazards, and support long-term reliability. Consistency in insulation thickness, compression ratio, and contact integrity ensures that all terminals perform uniformly, even in large-scale industrial or commercial applications.
Future Outlook: Integration with Smart Technologies
Looking ahead, cold-pressed insulated terminals are expected to integrate with smart monitoring and IoT systems. Embedded sensors could provide real-time feedback on current flow, temperature, and connection stability, enabling predictive maintenance and early fault detection. These features will support the development of intelligent electrical networks, from smart grids to automated factories. The combination of traditional mechanical reliability and emerging digital capabilities ensures that cold-pressed insulated terminals will remain vital for modern electrical systems.
Cold-Pressed Insulated Terminals continue to play a pivotal role in the development of safe, efficient, and sustainable electrical connections. Their durability, adaptability, and potential for smart integration make them a critical component across automotive, renewable energy, industrial, and consumer electronics applications.
News categories
Exhibition Information
Related Products

 +86-15558905711
+86-15558905711 +86-15057372736
+86-15057372736 [email protected]
[email protected] 105 Liuxiang Road, Liushi Town, Yueqing City, Wenzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
105 Liuxiang Road, Liushi Town, Yueqing City, Wenzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
 英语
英语 中文简体
中文简体 俄语
俄语 西班牙语
西班牙语











